Social engineering has emerged as one of the most dangerous threats in crypto today. In 2024, victims reported over $6.5 billion in losses to investment fraud, more than any other category of cybercrime, according to the
FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center. And in just one week of May 2025, on-chain sleuth ZachXBT uncovered an additional $45 million stolen from Coinbase users through social engineering scams. At the same time, attackers are increasingly harnessing AI to automate phishing at scale, generate deepfake audio to impersonate support agents, and craft ultra-convincing scam websites—making social engineering more insidious than ever. Unlike technical exploits, social engineering preys on human trust and emotion, making it alarmingly effective.
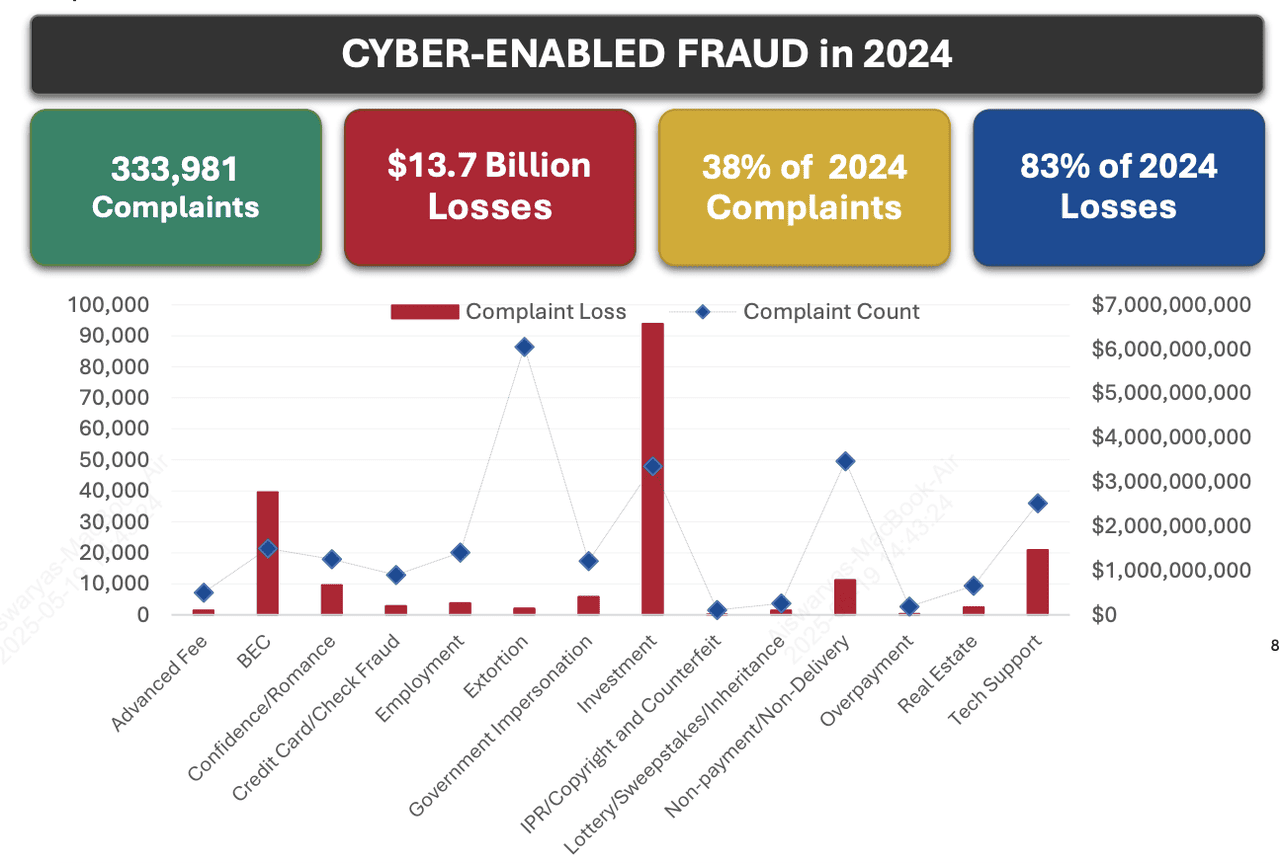
Cyber frauds in 2024 | Source: FBI
What makes these attacks especially perilous in crypto is the irreversible nature of blockchain transactions. Once you approve a transaction or reveal your
seed phrase, there’s no central authority to reverse the damage. That puts the burden squarely on you: vigilance and healthy skepticism are your best defenses against con artists who use fear, urgency, AI-driven personalization, and promises of easy gains to trick you into giving up control of your assets.
What Is Social Engineering?
At its core, social engineering is “posting content that tricks users into performing an action that users would do only for a trusted entity, such as revealing confidential information, downloading unwanted or malicious software,
phishing, or baiting.” In other words, it manipulates human psychology rather than exploiting code-based vulnerabilities.
Traditional hacking targets software flaws, such as buffer overflows, misconfigured servers, or zero-day bugs. Social engineering, by contrast, turns the human element into the weakest link. Attackers impersonate trusted figures, craft urgent messages, and exploit cognitive biases like fear and greed to bypass even the most robust technical defenses. Understanding this distinction is crucial: no code review or firewall can stop a well-crafted con that convinces you to hand over your keys or crypto assets.
Real-World Examples of Recent Social Engineering Attacks in Crypto
Before we dive into prevention tips, let’s look at a few real-world examples that show just how costly and widespread social engineering in crypto can be. These incidents highlight the bold tactics scammers use and the staggering losses suffered by unsuspecting users.
1. Coinbase Scams Cost $45 Million+ in One Week: In early May 2025, blockchain investigator
ZachXBT identified $45 million stolen from Coinbase users over just seven days, all through social engineering tactics such as phishing links and fake support messages, sharing his insights through his Telegram channel. These losses added to an annual total of over $300 million attributed to similar schemes on the platform.
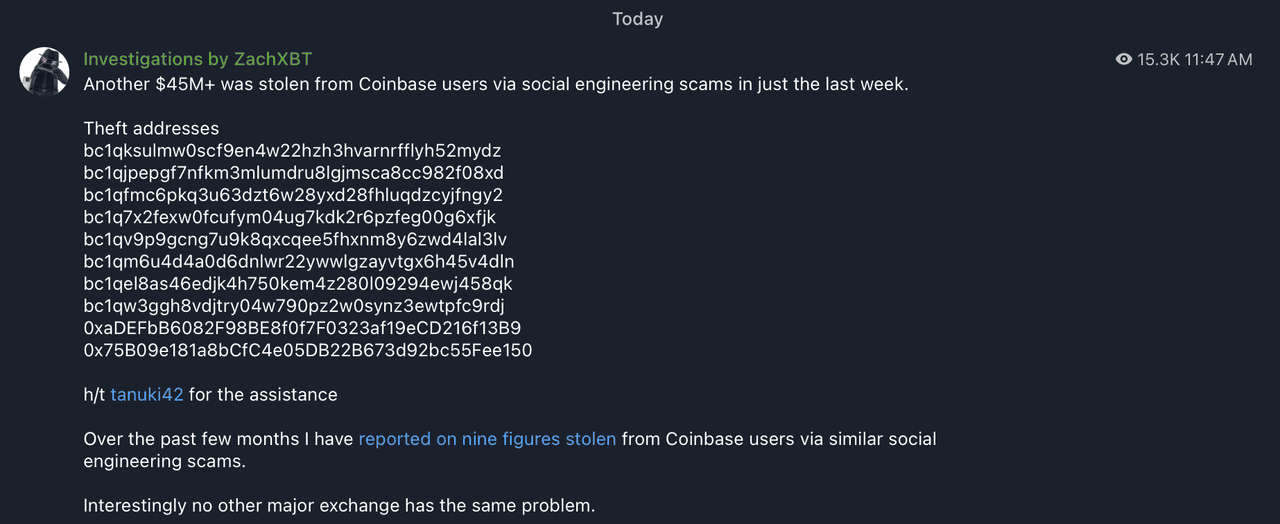
ZachXBT uncovers over $45M lost to social engineering scams by Coinbase users | Source: Cointelegraph
2. The Bybit Heist: $1.5 Billion Stolen in a Single Transfer: On February 21, 2025, Bybit fell victim to the largest crypto heist ever when attackers siphoned off roughly 401,000 ETH, worth about $1.5 billion at the time, during a routine cold-to-warm wallet transfer. Rather than exploiting code, the hackers used sophisticated phishing and social engineering to compromise the
multi-signature (multisig) signers, tricking them into approving a malicious transaction. This breach underscores that even “cold” or multisig storage isn’t immune if human workflows are targeted.
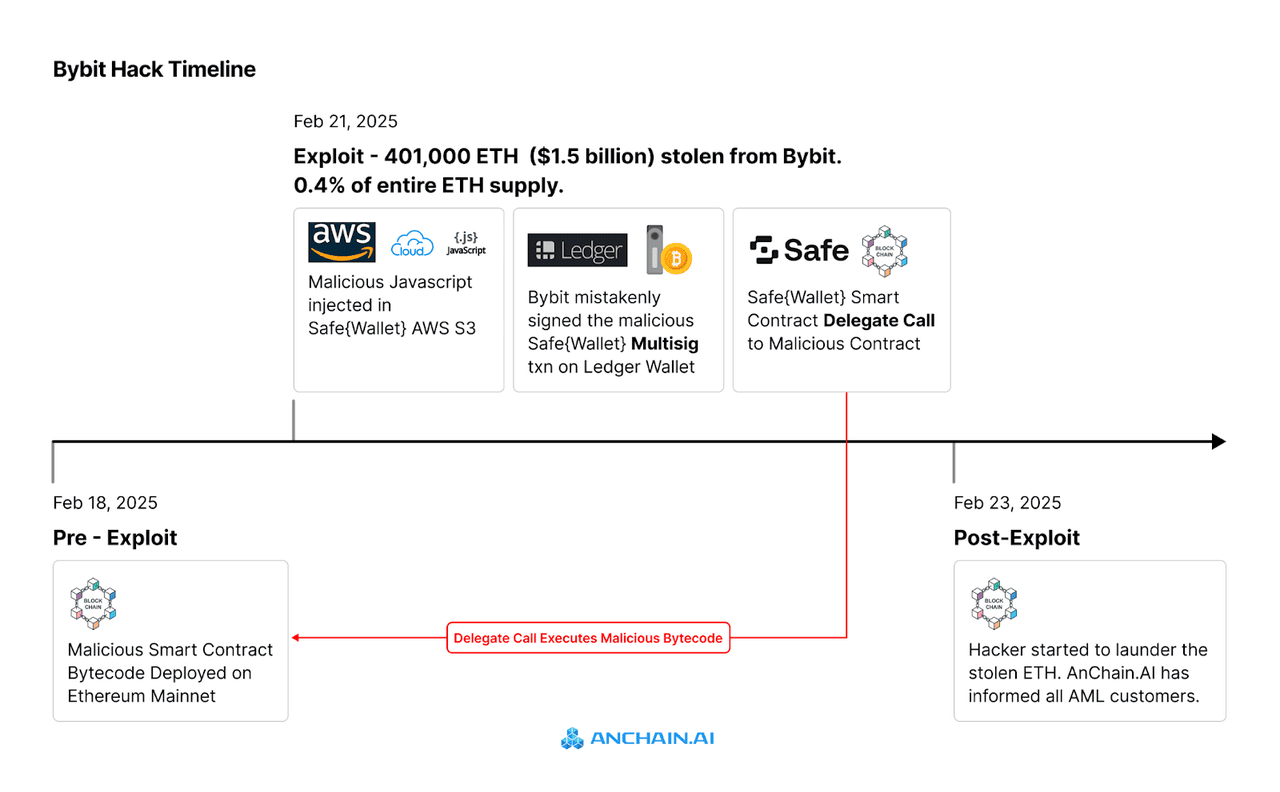
An overview of the Bybit hack | Source: Anchain.ai
3. Pig-Butchering Surge: $9.9 Billion in 2024: “Pig-butchering” scams, where attackers cultivate long-term trust before convincing victims to make large fake investments, drove at least
$9.9 billion in on-chain scam revenue in 2024, a 40% increase year-over-year, according to Chainalysis. Fraudsters are leveraging AI and highly professionalized tactics to scale these operations.
4. FBI Warnings: $6.5 Billion Lost to Crypto Investment Fraud: The
FBI’s 2024 Internet Crime Report shows that victims of investment fraud, primarily involving cryptocurrency, reported losses exceeding $6.5 billion, more than any other category of cybercrime. Phishing and spoofing were the top complaint types, highlighting how social engineering remains the dominant threat vector against crypto users.
How Does a Social Engineering Scam Work?
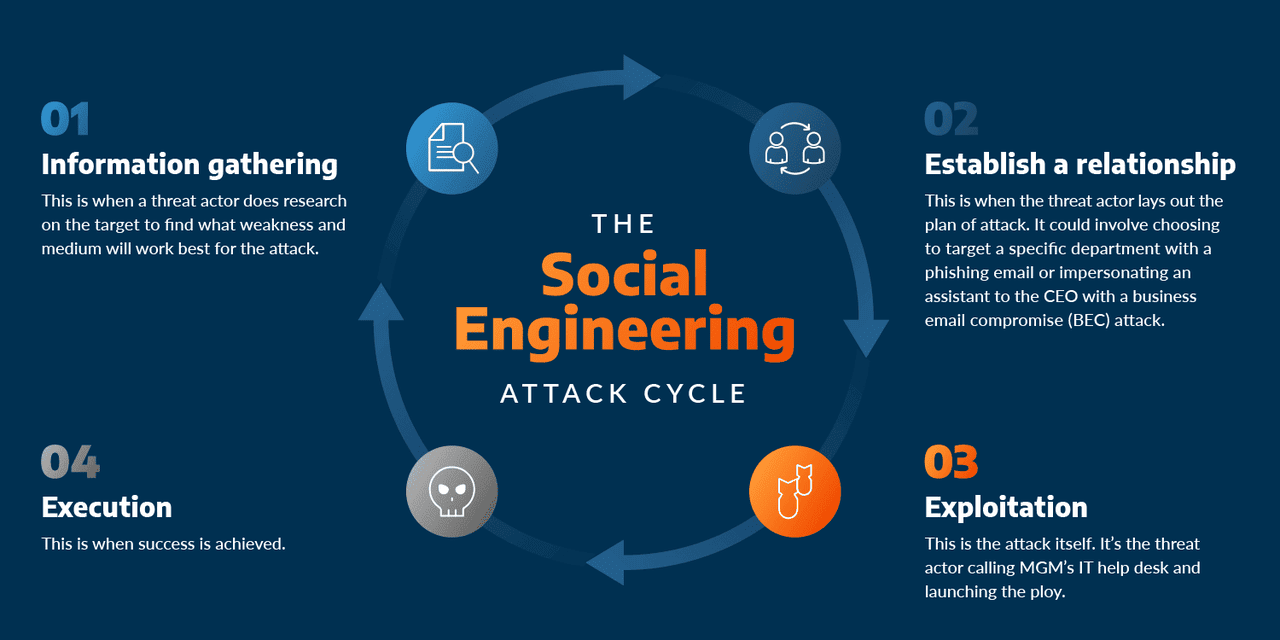
How a social engineering attack works | Source: ArcticWolf
Social engineering scams in crypto almost always follow a predictable playbook. By understanding each phase, you can spot red flags before the con artists spring their trap.
1. Setup: Scouting Targets: Scammers lurk on X, Telegram, Discord and other social channels, hunting for promising marks. They look for newbies asking for help, users bragging about big gains, free airdrops, and new projects, or anyone who’s accidentally shared a
wallet address or email. The more public information they gather, the more convincing their approach can be.
2. Approach: Gaining Trust: Next, they reach out under false pretenses, posing as support agents from
MetaMask or BingX, well-known influencers, or even community moderators. They clone profile pictures, tweak usernames, and may add fake verification badges to lower your guard. At this point, you think you’re interacting with someone legitimate.
3. Hook: Creating Urgency or Fear: With trust established, scammers pull the emotional trigger. You might receive messages like, “Your wallet will be frozen in 10 minutes!” or “Exclusive airdrop ends in 5 minutes - act now!” Fear of loss and
FOMO (fear of missing out) push you to act before you’ve had time to think.
4. Ask: Extracting Secrets: This is the tipping point. You’re asked to share your seed phrase or
private key “for verification,” click a link to an exchange-looking site, or approve a
smart contract that seems harmless. What looks like a small favor instantly hands over control of your wallet.
5. Heist: Draining & Laundering: Once scammers have your credentials or transaction approval, they empty your wallet at lightning speed. Funds are often swapped into privacy coins like
Monero and routed through mixers or lesser-known exchanges, making them nearly impossible to trace. Victims usually realize what happened only when it’s too late.
By recognizing these stages, you can spot the warning signs early and stop a social engineering attack before it succeeds.
Why Are Crypto Users Prime Targets for Social Engineering Attacks?
With crypto’s rapid growth, Bitcoin soaring to new all-time highs and total market capitalization crossing $3.25 trillion, vast sums now flow through blockchain networks. Scammers are also leveraging this boom (and many users’ inexperience) by exploiting key vulnerabilities in the following ways:
1. Irreversible Transactions on Blockchain Network: On most blockchains, once you approve a transfer, you can’t reverse it. That means a single mistaken click, such as approving a malicious contract or sending funds to a scam address, can cost you everything. There’s no “chargeback” or central bank to appeal to.
2. Blockchain's Inherent Decentralized Nature: Crypto’s decentralized design is a double-edged sword. Without a central authority, there’s no one to freeze or recover stolen assets. Scammers know this, and they exploit the fact that victims are on their own once funds leave their wallets.
3. High Stakes & Greed: The potential for huge, fast gains draws many into crypto. Social engineers weaponize this greed and FOMO (fear of missing out), dangling exclusive deals or “insider” opportunities. When you’re chasing quick profits, it’s easy to overlook red flags.
4. Knowledge Gaps: Many newcomers lack basic security know-how. They may not understand seed phrases, phishing URLs, or the importance of
two-factor authentication. Scammers prey on this ignorance, targeting users who aren’t familiar with simple vigilance practices.
What Are the Common Types of Crypto Social Engineering Scams?
Next, we’ll explore the key factors that make you vulnerable and the most common tactics scammers use to exploit those weaknesses.
1. Phishing: Scammers build fake wallet apps or exchange sites that look identical to the real thing. You enter your seed phrase or private keys, and hand over your entire balance. For example, a sham MetaMask pop-up can trick you into revealing your recovery phrase.
2. Impersonation: Attackers pose as support agents, influencers, or even friends. They copy profile pictures and usernames, then message you with urgent requests. A fake “BingX support” rep might claim your account is compromised and ask for your credentials.
3. Giveaway Scams: “If you send 1 ETH, you’ll get 2 ETH back!” These classic
rug pulls lure you with promises of free money. Once you send your ETH to claim the “gift,” the scammer disappears, and your funds are gone for good.
4. Romance & “Pig Butchering”: In these
long-con scams, attackers spend weeks or months building trust. They feign romance or friendship, then introduce a “can’t-miss” investment opportunity. Victims often send large sums before realizing they’ve been duped.
5. Fake Investment Platforms: Fraudsters clone
DeFi dashboards or launch bogus
staking sites promising absurd yields. You stake your tokens, watch your “balance” grow on-screen, and then find you can’t withdraw a single satoshi when you try.
Each of these scams relies on psychological manipulation. By understanding how they operate, you can spot the warning signs, and keep your crypto safe.
How to Stay Safe From Social Engineering Attacks
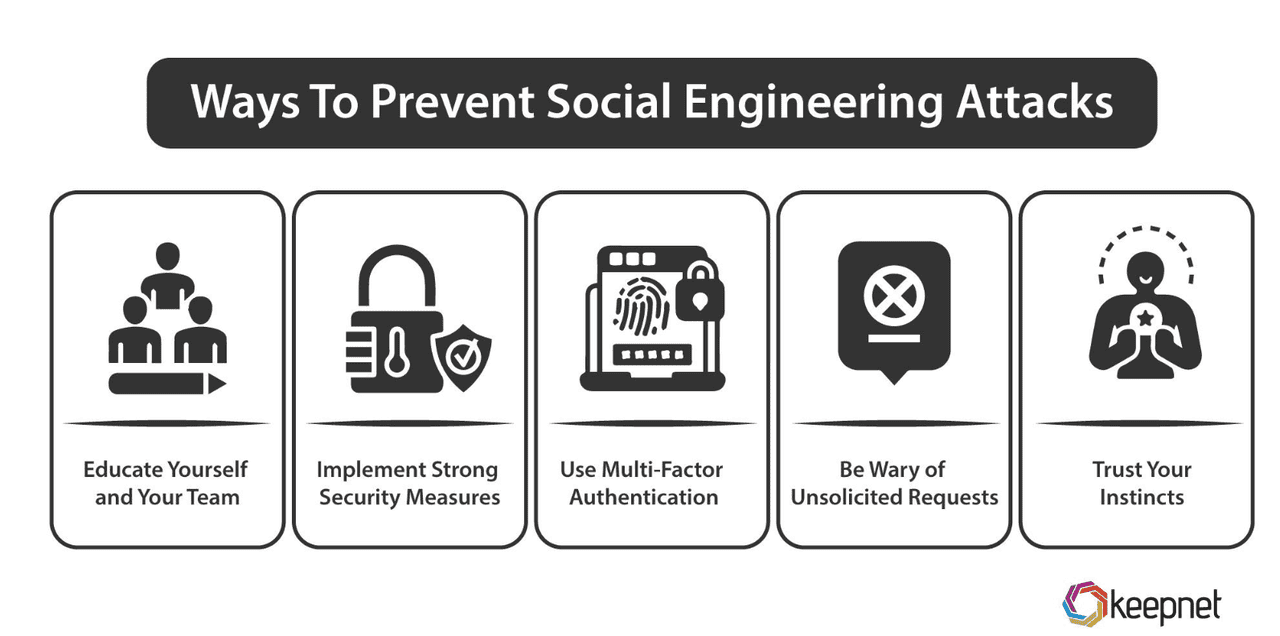
How to prevent social engineering attacks | Source: keepnet
Protecting yourself from social engineering attacks doesn’t require advanced tech skills; small, consistent habits can stop most scams in their tracks. Below are five practical steps you can take today to keep your crypto safe.
1. Be Skeptical of Unsolicited Contacts: Treat any unexpected message, whether on X, Telegram, email, or SMS, with caution. If someone claiming to be “BingX Support” reaches out about a “security issue,” don’t click their link. Instead, open your browser and visit the official BingX site or app to check for alerts.
2. Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Always turn on 2FA for your exchange and wallet accounts, ideally using a hardware key (if supported, like a YubiKey) or an authenticator app (Google Authenticator, Authy). This way, even if a scammer steals your password, they won’t be able to access your account without your second factor.
3. Verify URLs & Links Before Clicking on Then: Hover over every link before clicking to see the real URL. Bookmark the official login pages of your wallets and exchanges to avoid phishing clones. For instance, a fake MetaMask site might use “metamask-login[.]com” instead of “metamask[.]io.” Always check for subtle typos.
4. Use Hardware Wallets for HODLing Your Crypto Assets: Store the bulk of your crypto on a
hardware wallet (
Ledger, Trezor, etc.) that keeps private keys offline. Only transfer small amounts to software wallets when you need them. Even if you accidentally approve a malicious contract on your desktop wallet, an attacker can’t drain assets locked in your offline hardware device.
5. Regularly Update Software & Firmware: Keep your wallets, apps, and devices patched with the latest security updates. Developers release fixes for newly discovered vulnerabilities; ignoring them is like leaving your front door unlocked.
6. Educate Yourself Continuously: Follow trusted security blogs (e.g., Krebs on Security, NIST updates) and official exchange advisories. Regularly review basic guides on spotting phishing, baiting, and other con tactics. You can also follow
BingX Academy to stay updated on the latest scam trends and preventative best practices.
By embedding these simple habits into your routine, you’ll dramatically reduce the risk of falling prey to social engineering scams. Vigilance and education are your strongest defenses in the decentralized world of crypto.
Final Thoughts
In the decentralized world of crypto, your human firewall is your strongest asset. Stay vigilant by questioning unsolicited requests, verifying every link and login page, educating yourself on the latest scam tactics. Always remember: if it sounds too good to be true, it probably is. Combine these habits with technical safeguards, like 2FA, hardware wallets, and software updates, and you’ll be well-equipped to navigate the crypto space safely.
Related Reading

 Cyber frauds in 2024 | Source: FBI
Cyber frauds in 2024 | Source: FBI ZachXBT uncovers over $45M lost to social engineering scams by Coinbase users | Source: Cointelegraph
ZachXBT uncovers over $45M lost to social engineering scams by Coinbase users | Source: Cointelegraph An overview of the Bybit hack | Source: Anchain.ai
An overview of the Bybit hack | Source: Anchain.ai How a social engineering attack works | Source: ArcticWolf
How a social engineering attack works | Source: ArcticWolf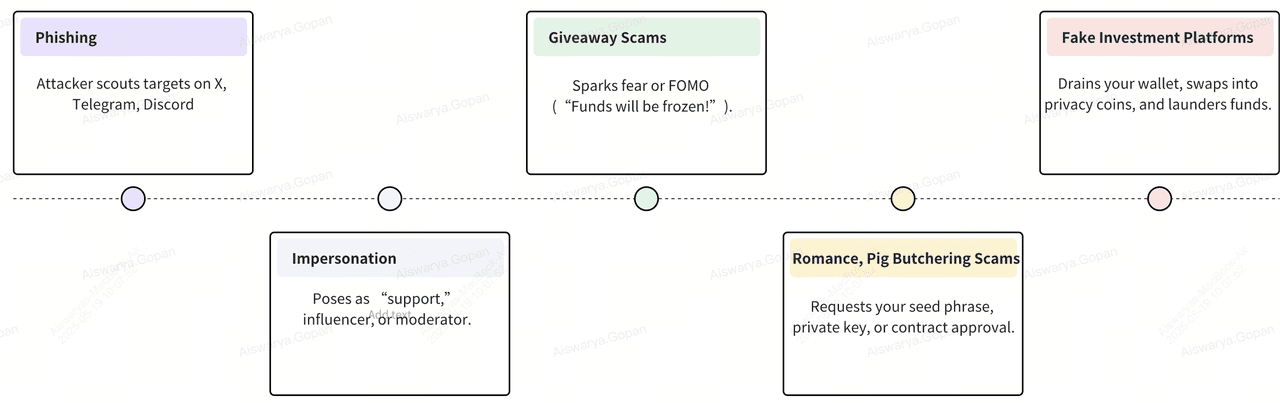
 How to prevent social engineering attacks | Source: keepnet
How to prevent social engineering attacks | Source: keepnet

