Phishing scams are accelerating across crypto, and getting smarter with
AI. CertiK’s 2024 review attributes $1.05 billion in losses to 296 phishing incidents alone, making it the year’s costliest attack vector. In 2025, stolen funds have already exceeded $2.17 billion by November, driven by large exchange breaches and increasingly sophisticated
social engineering, including AI-assisted lures and deepfakes.
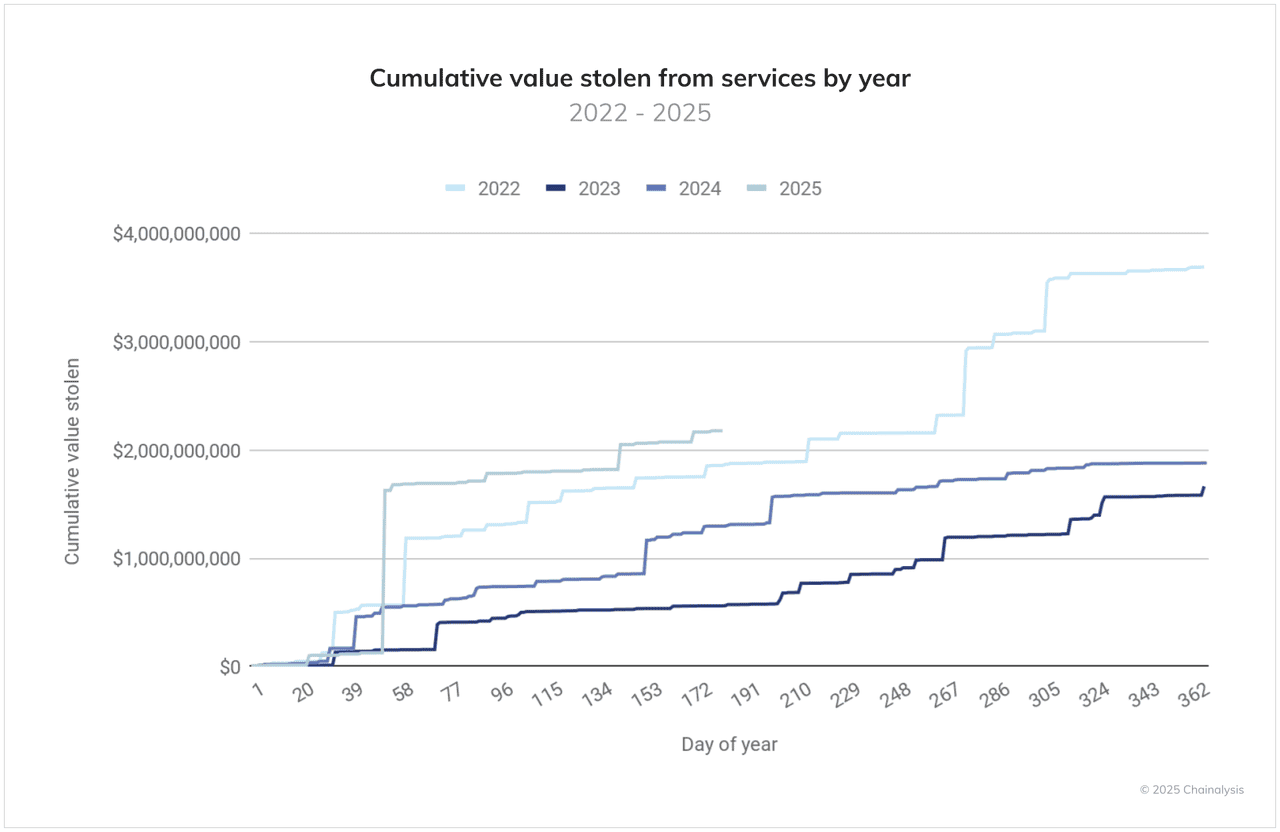
Cumulative value stolen from from services between 2022 and 2025 | Source: Chainalysis
Chainalysis and Reuters both flag GenAI as a key force behind record scam revenues at least $9.9 billion in 2024, while compliance data show social-engineering scams account for 40.8% of this year’s security incidents, well ahead of pure technical exploits. A stark example: a single victim lost 783 BTC valued at around $91 million in August 2025 after being conned by a fake
hardware-wallet “support” agent.
As a BingX user, that context matters: scammers now blend look-alike sites, spoofed support, WhatsApp/Telegram impersonation, and AI-generated voices to rush you into mistakes.
This guide explains how crypto phishing works, how to spot red flags fast, and which
BingX security controls like anti-phishing code, withdrawal whitelist, emergency account lock help keep your funds safe, so you can trade with confidence.
What Is a Crypto Phishing Scam?
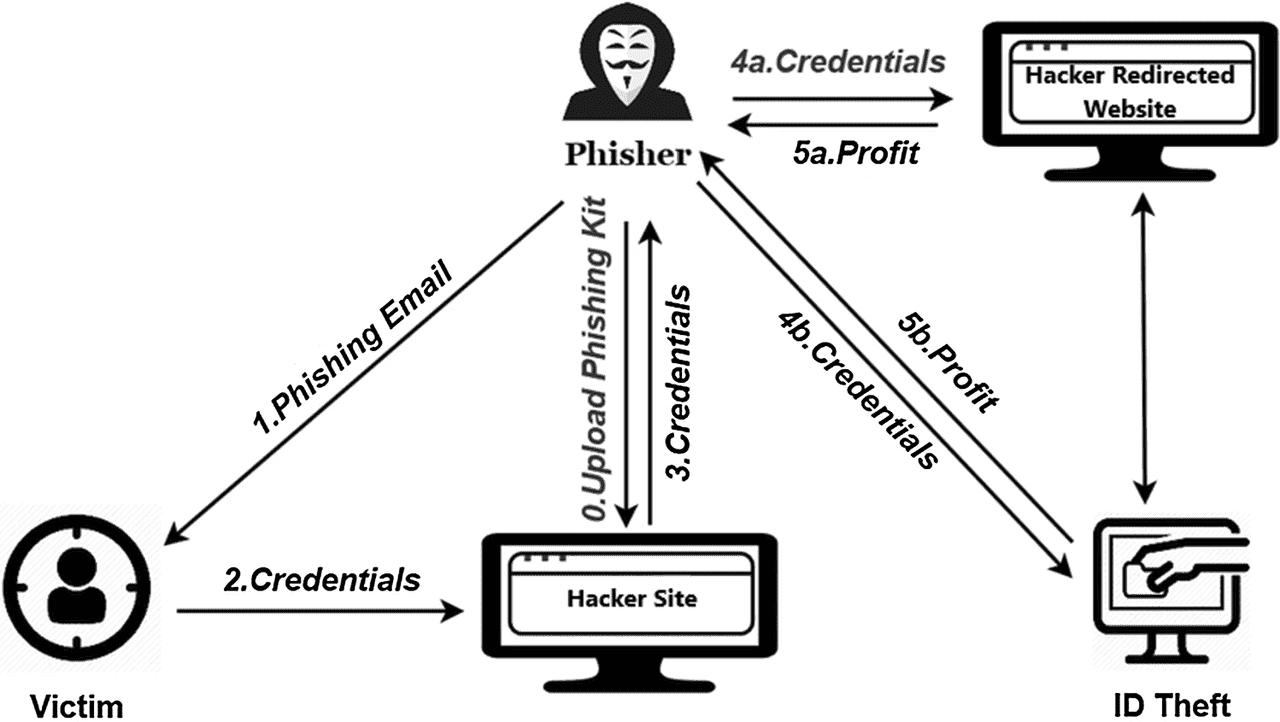
A crypto phishing scam is a type of cyberattack where scammers pretend to be someone you trust, like a crypto exchange, wallet provider, or customer support agent, to steal your sensitive information. Their goal is to gain access to your private keys, wallet seed phrases, or account login credentials so they can take control of your crypto assets.
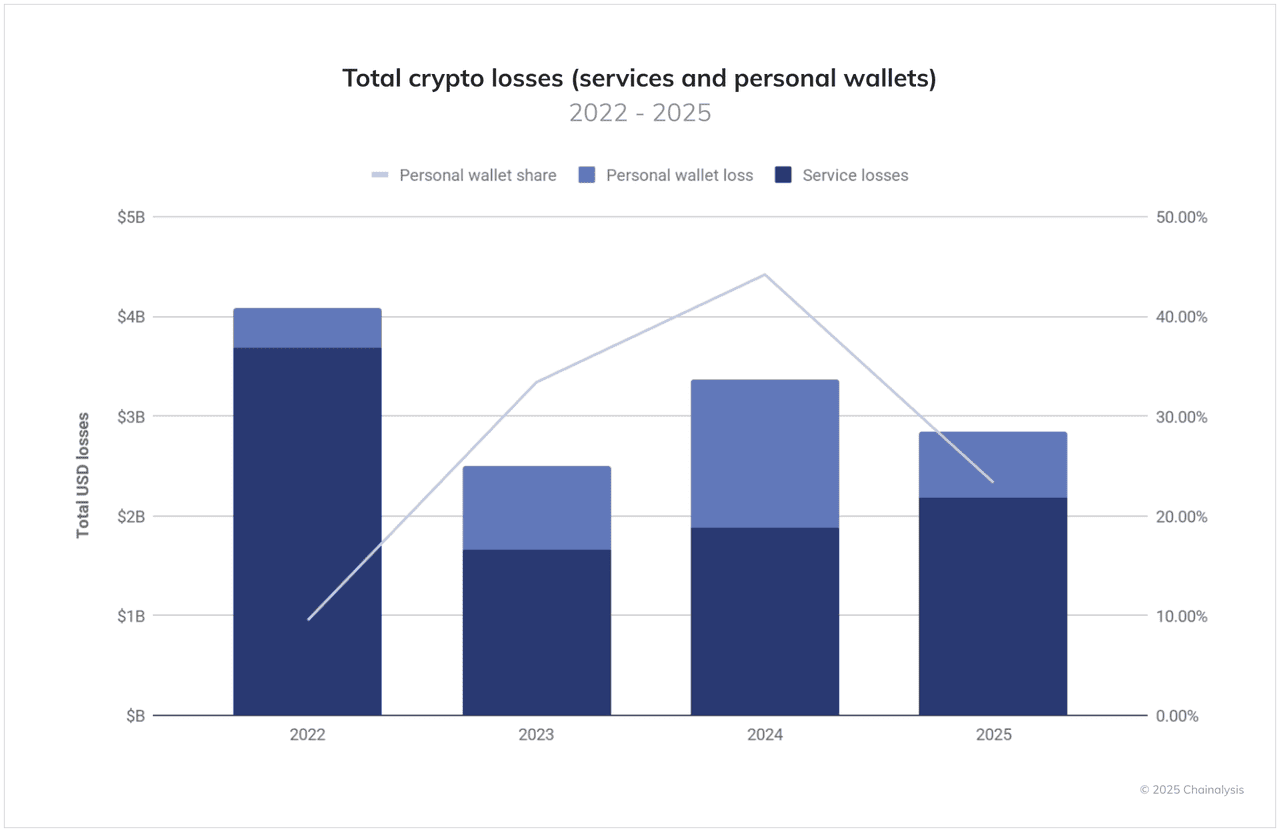
Total crypto losses, including services and personal wallets | Source: Chainalysis
Different Forms of Phishing Attacks
• Email phishing: Scammers send look-alike emails with urgent warnings and links to fake login or password-reset pages designed to steal your credentials. It was the top crypto loss vector in 2024, according to security firms.
• Smishing (SMS): Fake texts contain shortened or look-alike URLs that claim to verify your account or offer airdrops, but redirect to credential-stealing sites. These attacks target users who trust mobile alerts.
• Vishing (voice): Spoofed caller IDs, and now AI voice clones, pretend to be customer support and trick victims into revealing
2FA (two-factor authentication) codes or seed phrases. Social-engineering voice scams have been one of 2025’s biggest drivers of losses.
• Fake pop-ups/overlays: Malicious pop-ups on typosquatted or infected websites ask users to “re-enter” wallet passwords or perform fake security checks to harvest sensitive data.
• Address-poisoning/zero-value transfers: Attackers send zero-value transactions from look-alike wallet addresses, hoping you copy the wrong one later; one victim lost roughly $91 million in BTC to this tactic.
• App/IM impersonation: Scammers create fake WhatsApp or Telegram accounts with official branding to ask for funds or private keys, even though legitimate platforms publicly warn they will never DM users with investment opportunities.
What Are Some Common Types of Crypto Phishing Scams?
Phishing scams in crypto are becoming more advanced each year. Chainalysis and CertiK both reported record-high phishing losses in early 2025, with over $2.17 billion stolen in the first half of the year alone through a mix of email traps, fake websites, AI-generated calls, and wallet-poisoning attacks. These scams all aim to steal your login credentials, seed phrase, or on-chain signing approvals.
Below are examples of some of the most common phishing attacks and how they operate.
1. Fake Emails: Email Phishing
Example of an email phishing attempt
Email remains one of the most effective phishing tools because scammers can easily make messages look official. They copy logos, colors, and writing styles from trusted platforms, sometimes even faking the sender name.
You might receive an email saying:
• “Suspicious login detected”
• “Your withdrawal is on hold”
• “Verify your account to avoid suspension”
The email includes a link to a fake login page. Once you enter your password or 2FA code, the attacker steals it and immediately drains your account.
Data check: CertiK reported that phishing was the #1 attack vector in 2024, accounting for over $1.05 billion in losses till November 2025, and email phishing remains the primary entry point.
Safety Tip: Always check the sender’s full email address and look for spelling errors. If in doubt, go directly to the official site instead of clicking email links.
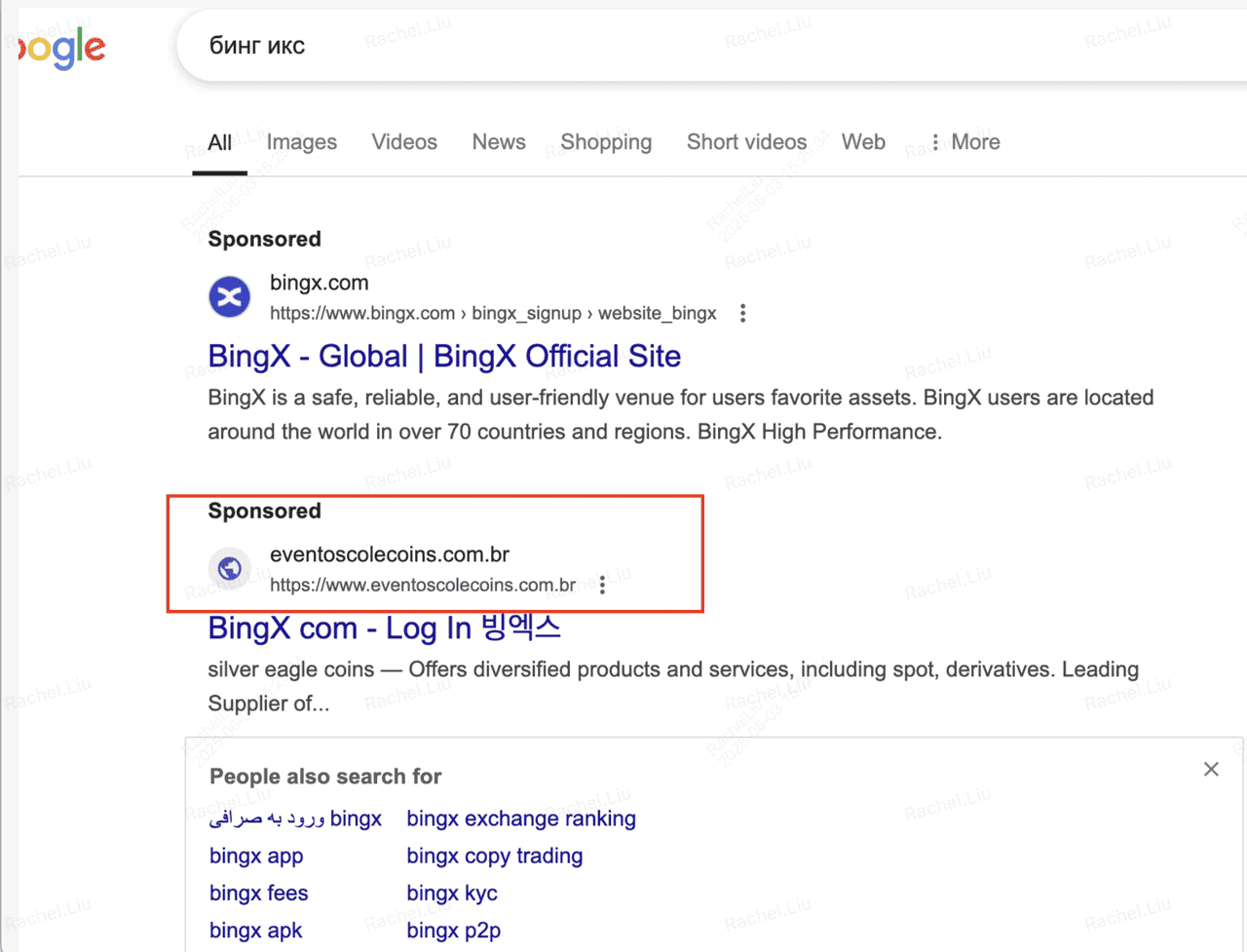
2. Fake Websites: Copycat Sites and URL Spoofing
Example of URL spoofing phishing attack
Scammers build fake login pages that look nearly identical to real exchanges. They often use URLs that are one or two characters off from the real domain; for example:
• bingx-secure.com
• bıngx.com (using a different character)
• bingx-app.help
If you enter your login details, seed phrase, or 2FA code, attackers gain full access to your wallet or exchange account.
Real example: A 2025 study published on arXiv by researchers from The Hong Kong Polytechnic University and UC San Diego analyzed over 6,600 address-poisoning incidents across Ethereum and BNB Chain, estimating more than $83.8 million in losses linked to look-alike URLs and fake wallet interfaces.
Safety Tip: Bookmark the official BingX website and only log in from saved bookmarks. Double-check every URL before entering credentials.
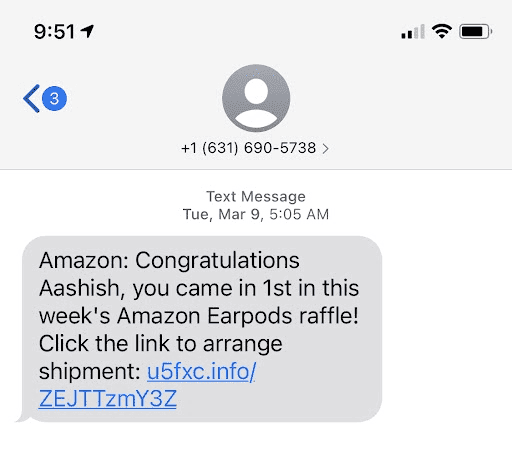
3. Smishing or SMS Phishing
Example of a smishing (SMS phishing) attack | Source: Berkeley IT Lab
Smishing happens through text messages designed to scare you into urgent action. These messages may claim:
• Your account is locked
• Your withdrawal failed
• You qualify for a free airdrop
The SMS includes a short URL (like bit.ly or tinyurl links) leading to a malicious website.
Why smishing attacks work: People trust mobile alerts more than email, so they react quickly, and scammers play on that urgency.
Safety Tip: Never click SMS links claiming to fix account issues. Instead, open the BingX app or website directly and check for notifications there.
4. Vishing or Voice Phishing
Vishing scams come through phone calls from someone pretending to be “BingX Support,” “Exchange Security Team,” or even your bank. They claim there is a problem with your account and ask for:
• 2FA codes
• Passwords
• Wallet seed phrases
• Remote device access
Thanks to AI, scammers now use voice-cloning to sound like real support agents—or even like someone you know.
Data point: According to WhiteBIT’s 2025 security report, social-engineering scams (including vishing) made up 40.8% of crypto security incidents this year.
Warning: BingX will never call you to request a password, verification code, or seed phrase. If someone calls asking for them, hang up immediately.
5. Zero-Value Transfers and Address Poisoning
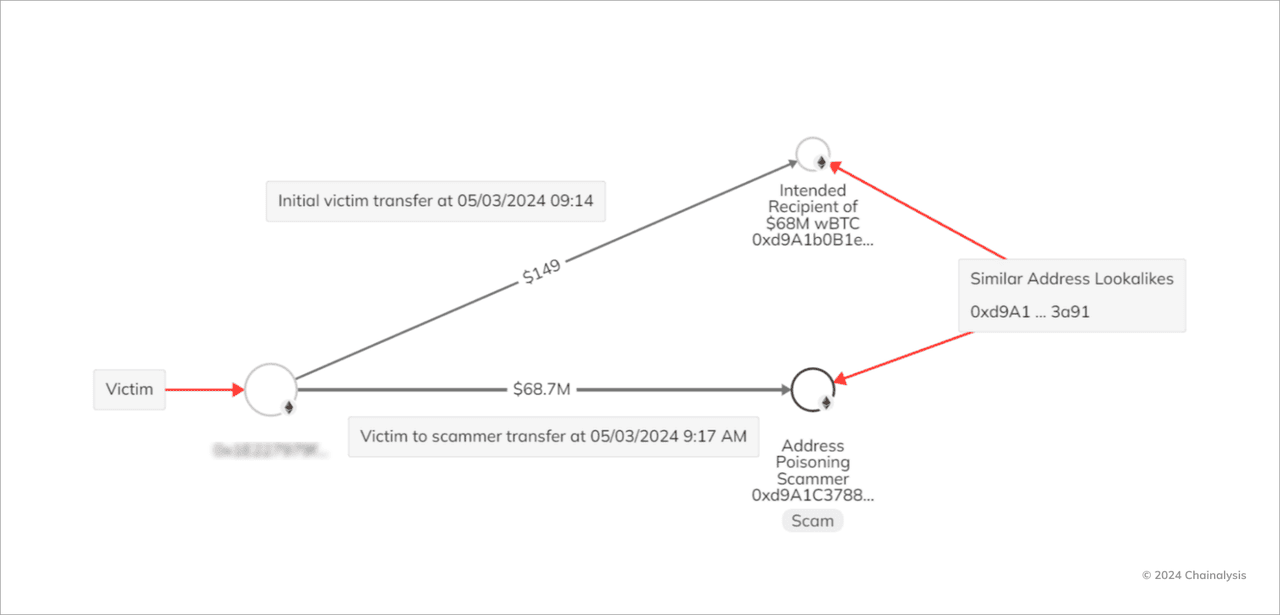
How an address poisoning scam works | Source: Chainalysis
This scam targets your transaction history, not your inbox. Attackers send a zero-value transaction to your wallet from an address that looks almost identical to one you trust. Later, when you copy a previous address to send funds, you might accidentally pick the scammer’s fake one.
Real Example: A victim lost $91M in Bitcoin (783 BTC) in August 2025 after falling for this trick twice during large transfers. Blockchain analysts confirmed the attacker exploited address-poisoning to intercept funds.
Safety Tip: Never rely on just the first and last few characters of a wallet address. Use a trusted address book or manually verify the entire address before sending.
6. AI-Powered Phishing Attacks
How an AI-powered phishing scam operates | Source: WeSecureApp
Artificial Intelligence has changed the phishing landscape. Attackers now use AI chatbots, voice clones, and deepfake videos to make scams more realistic and harder to detect. According to the Chainalysis 2025 Crypto Crime Report,
AI-driven phishing helped push crypto scam revenues to at least $9.9 billion in 2024, and analysts report a sharp increase in 2025 as scammers scale attacks faster than before.
AI tools allow scammers to:
• Generate realistic customer-support chats that copy official tone and formatting
• Create deepfake voice calls that sound like real exchange agents or even friends
• Personalize phishing emails using leaked data like names, regions, or login history
These attacks feel “legitimate” because they look human, respond in real-time, and mimic how real support teams speak. Some even include fake anti-phishing codes and warnings about “suspicious account activity” to pressure users into clicking malicious links.
Security Reminder: If a message feels unusually personalized, requests urgent verification, or pushes you to click fast, pause. Always verify through the official app or website instead of responding to emails, pop-ups, DMs, or calls.
7. Telegram Phishing via Fake Bots and Admins
Example of Telegram phishing attack | Source: Bank of Singapore
Telegram is a major hub for crypto communities, but also a major target for phishing. Scammers frequently create fake “support bots” or impersonate project admins to lure users into sharing wallet credentials. According to the WhiteBIT 2025 security report, messaging-platform scams, especially on Telegram, made up over 10% of all crypto phishing incidents, with attackers pretending to fix “deposit errors” or “withdrawal failures.”
A typical scam looks like this:
• A fake bot DMs you after you join a crypto group
• It claims there was a processing error with your deposit or KYC
• It asks for your seed phrase or directs you to a fake “support portal”
Once a seed phrase or private key is entered, funds are typically stolen within minutes.
Safety Tip: No exchange or support team will DM you first. Real staff never ask for seed phrases or wallet exports. Always verify admins by checking the official group channel.
8. App Store Phishing: Fake Apps
Fake crypto app listing on an app store | Source: Sophos
Fraudsters also disguise malware as “wallet apps,” “portfolio trackers,” or fake versions of real trading platforms. Some appear on third-party Android stores, while others temporarily slip into official app stores before being reported. These apps capture login credentials, log keystrokes, or mimic wallet interfaces to approve unauthorized transfers.
Cybersecurity firm Sophos has reported multiple 2025 cases where fake wallet apps harvested private keys and sent them directly to attacker-controlled servers. In many incidents, users believed they were using the official app, because the interface looked identical.
Safety Tip: Always download apps from trusted sources like the official website, Apple App Store, or Google Play Store. Double-check the developer name and reviews before installing.
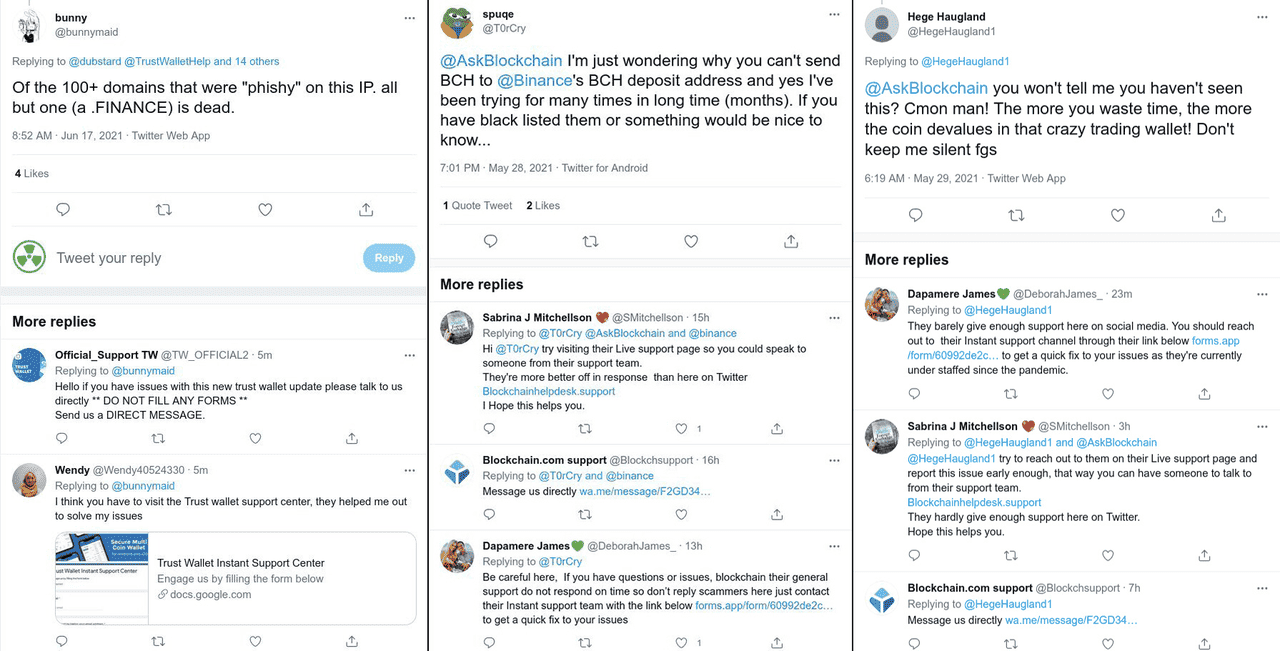
9. Social Media Phishing: Fake X/Twitter Accounts and Giveaways
Example of a Twitter/X phishing scam | Source: Kaspersky
X (formerly Twitter) is widely used for crypto announcements, but scammers exploit it to promote fake airdrops and giveaways. Attackers impersonate exchanges, founders, or influencers and post links that request wallet connections, private keys, or transaction signatures.
These scams often include:
• Fake verified-looking profiles
• Screenshots showing “successful rewards”
• QR codes or phishing links to counterfeit event pages
Once a wallet connects or signs a malicious contract, attackers can drain funds or take token approvals. Chainalysis and cybersecurity researchers warn that social-engineering scams, especially fake giveaway links, continue to be a leading driver of wallet-drainer losses in 2025.
Safety Tip: Never trust giveaway links in replies or DMs. Always confirm news on an exchange’s official website or verified social-media profile.
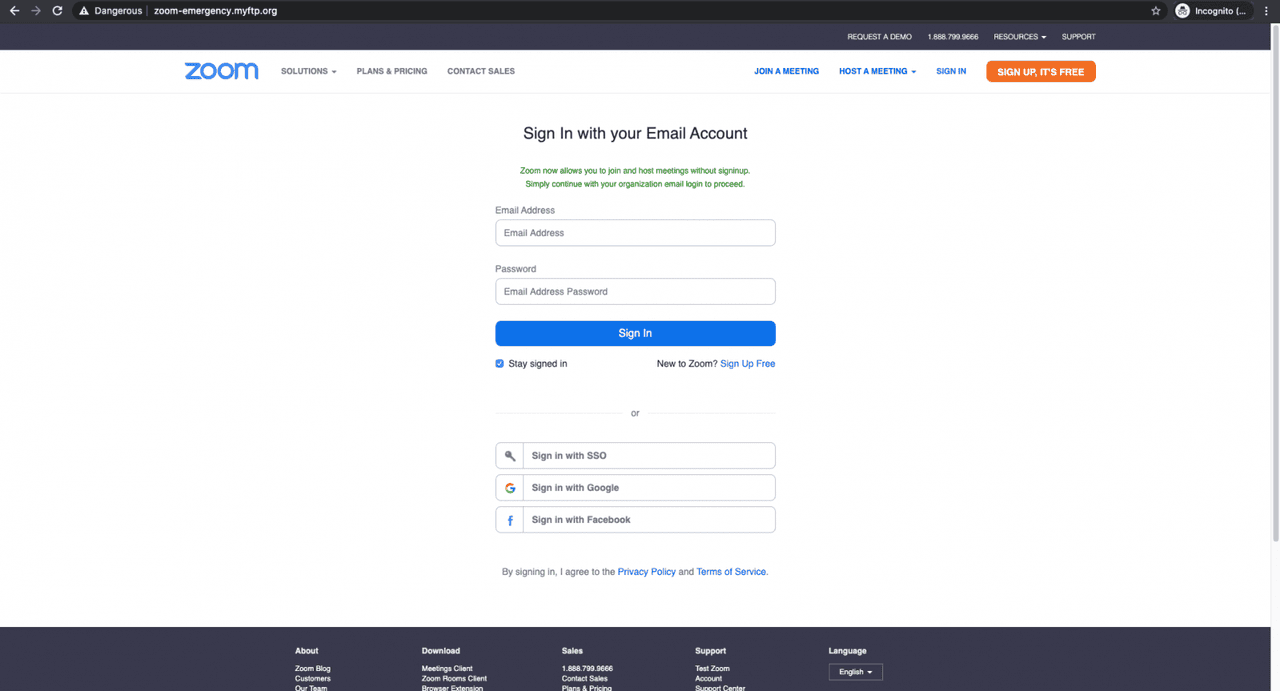
10. Fake Chat App Phishing: Zoom or WhatsApp Impersonation
Example of a Zoom phishing scam | Source: BleepingComputer
Scammers increasingly use Zoom, WhatsApp, and other chat apps to impersonate support or investment advisors. They may send a calendar invite or message offering “portfolio reviews” or claim your account has a problem that needs urgent attention.
A common tactic:
• Attacker invites a user to a Zoom call
• Pretends to troubleshoot an account issue
• Asks the user to log in on-screen or share a 2FA code
• Funds are stolen minutes after the login
Security researchers warn that deepfake video and voice tools make these scams more convincing in 2025.
Safety Tip: Exchanges do not schedule account recovery or
KYC verification calls through Zoom, WhatsApp, or private chat apps. If someone asks to screen-share or requests codes during a call, disconnect and report immediately.
Why Do Phishing Attacks Succeed?
Phishing works because attackers target human psychology, not just technology. Chainalysis notes that social-engineering scams were the fastest-growing crypto threat in 2025, driven by fear, urgency, and fake familiarity. Scammers make users believe something bad will happen, like account suspension or frozen funds, unless they act immediately. When panic sets in, people click before thinking.
In crypto, phishing has an extra advantage: transactions are irreversible. Once a seed phrase, 2FA code, or wallet signature is leaked, funds can be moved across mixers or cross-chain bridges within seconds, making recovery nearly impossible. This is why scammers prefer phishing over hacking, stealing credentials is easier and cheaper than exploiting code.
Another key factor is realism. AI now helps scammers generate emails, phone calls, and chat messages that look and sound exactly like a legitimate support agent. Some attacks even mirror your writing style or use personal details leaked from previous breaches. According to the 2025 Chainalysis Crypto Crime Report, these AI-assisted tactics helped push scam revenues to at least $9.9 billion in 2024, continuing upward into 2025.
The good news: once you know how phishing works, the traps become easier to spot. The next section shows exactly what to look for, so you can pause, verify, and protect your assets.
How to Spot a Phishing Scam: Top Tips
Even highly convincing messages reveal clues if you slow down and check the details. Here are the most common red flags:
1. Generic Greetings and Urgent Language: Phishing messages often start with “Dear user,” “Account holder,” or no greeting at all. They try to create panic with phrases like:
• “Your account will be locked”
• “Immediate verification required”
• “Unusual login detected”
This sense of urgency is intentional. Security researchers note that most successful crypto phishing scams begin with a time-pressure trigger, pushing victims to react before thinking.
If a message demands instant action, stop and verify through the official app or website.
2. Grammar or Formatting Errors: Professional exchanges proofread everything. Scam messages often contain:
• Misspellings
• Strange punctuation
• Odd sentence structure
• Inconsistent fonts or spacing
These errors appear because many phishing operations are automated or translated poorly.
If the wording feels “off,” treat the message as suspicious.
3. Mismatched Links, Short URLs, or Look-Alike Domains: Before clicking, always inspect a link. Scammers frequently use:
• URL shorteners (bit.ly, tinyurl)
• Extra characters (bingx-service.com, bıngx.com)
• Misspelled domains that look close to the real one
A 2025 academic review on wallet-poisoning attacks found that fake URLs and interface spoofing contributed to tens of millions in stolen crypto, often because users clicked without checking.
Hover to preview links. If it’s not bingx.com, don’t open it.
4. Fake Senders or Spoofed IDs: Phishers send emails from addresses that look official at a glance, such as:
• support@bingx-helpdesk.com
• service@bıngx.com
• bingx-security@outlook.com
They also spoof SMS sender names so messages appear to come from a trusted platform.
Always check the full email address, and not just the display name. If unsure, open the official app instead of the message.
How to Avoid Phishing Crypto Scams as a BingX User
Staying safe in crypto comes down to two things: smart habits and using the security tools built into BingX. Phishing attacks have become more advanced, especially with AI-powered scams, but a few practical steps dramatically reduce risk.
1. Maintain Personal Vigilance
• Bookmark Official Sites: Always access BingX from the official domain: https://www.bingx.com. Chainalysis notes that thousands of victims per month lose funds after clicking phishing links disguised as login pages or airdrops. Bookmarking removes that risk.
• Use Strong, Unique Passwords: Many crypto breaches begin when attackers reuse leaked passwords from unrelated sites. Security researchers warn that reused passwords are a leading cause of exchange account takeovers. Use a password manager to generate and store complex passwords.
• Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Turning on 2FA blocks most unauthorized logins, especially automated bot attacks and credential stuffing. Industry reports show that accounts with 2FA are over 90% less likely to be compromised.
• Keep Devices Updated: Outdated phones, browsers, and apps are easier to exploit. Software updates often include security patches that shut down new malware and phishing tools.
• Avoid Public Wi-Fi or Use a VPN: Public networks are easy to monitor, and attackers can intercept login data. If you must use public Wi-Fi, use a trusted VPN to encrypt traffic.
2. Use BingX-Specific Security Features
BingX provides multiple layers of protection to help stop phishing attacks, even if scammers get your password.
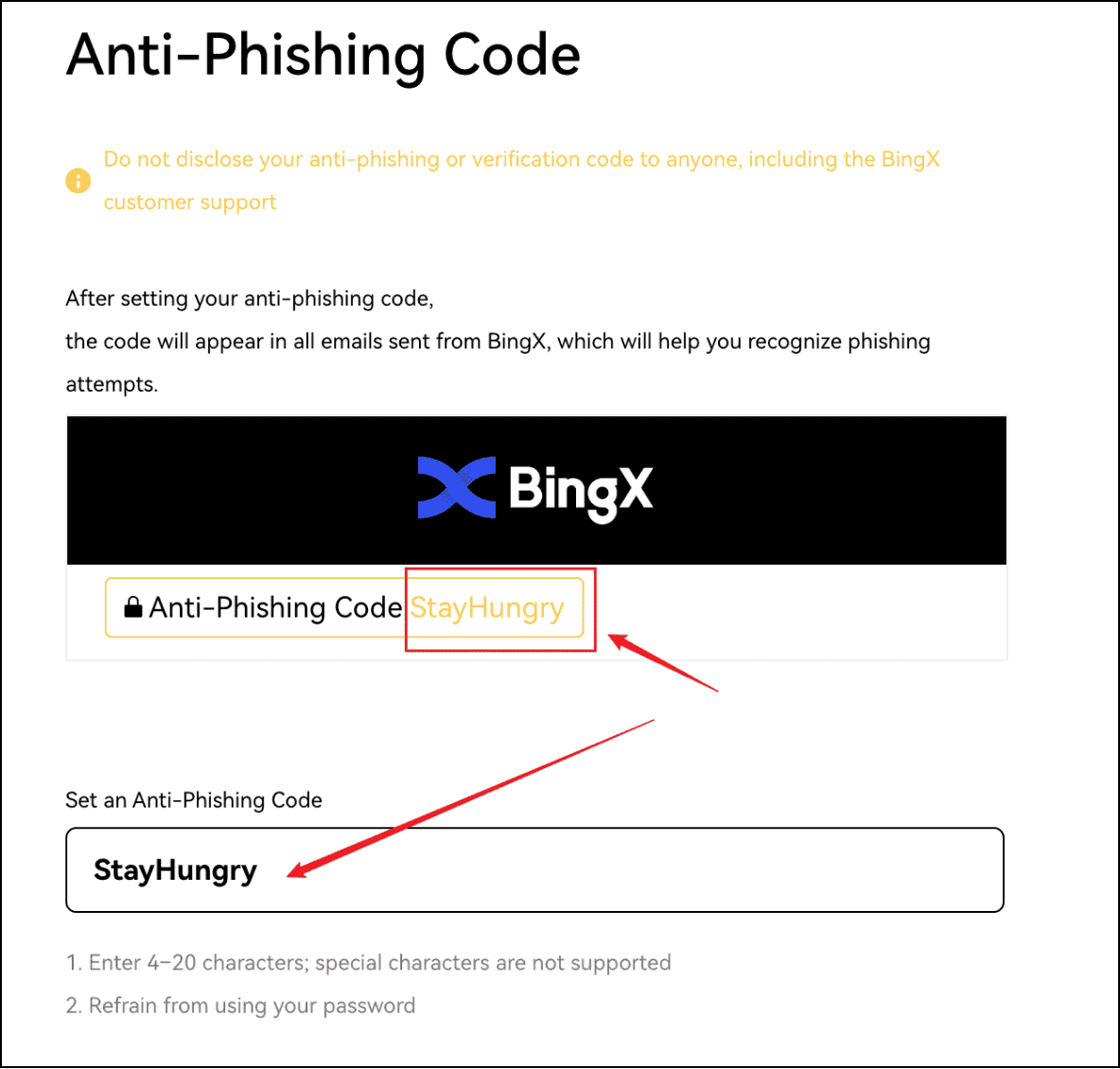
BingX anti-phishing code
1. Set Up an Anti-Phishing Code: When enabled, a personalized code appears in all official BingX emails. If an email is missing the code, it’s likely fake. You can activate this in Account & Security → Anti-Phishing Code.
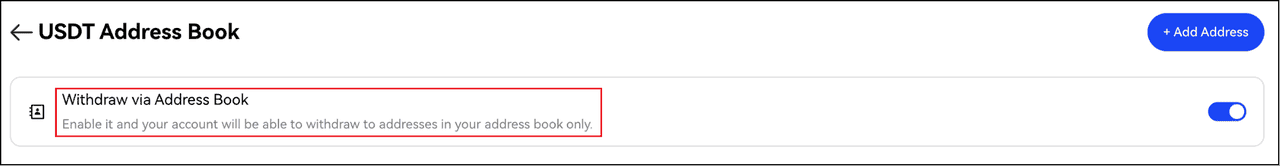
Withdrawal whitelist on BingX
2. Enable Withdrawal Whitelist: This feature lets you pre-approve safe wallet addresses. Even if someone gets into your account, they cannot withdraw to a new or unknown address. Go to Account & Security → Withdrawal Whitelist to turn it on.
How to lock your BingX account on suspicious activity
3. One-Click Account Lock: If you notice strange login attempts or unauthorized actions, BingX lets you freeze your account instantly. This stops withdrawals, API usage, and active sessions.
BingX Verify
4. Verify Official Channels: Only download the BingX app from the Apple App Store, Google Play, or the official website. If you need to confirm whether a page, domain, or social account is real, use BingX Verify, a tool designed to identify official URLs and support portals.
3. Leverage BingX's Platform-Level Authentication
Behind the scenes, BingX uses advanced email-security protocols including DKIM, SPF, and DMARC. These standards help prevent scammers from spoofing @bingx.com emails and ensure that official messages truly come from the platform.
However, technology alone isn’t enough; your awareness still plays the biggest role. Always double-check URLs, never share seed phrases, and be cautious with DMs or “urgent account alerts.”
What to Do If You Suspect a Phishing Scam
If something feels wrong, act immediately. Fast response can stop attackers from moving funds.
1. Disconnect Immediately: Change your passwords starting with BingX and your email. Revoke login sessions on other devices and scan for malware before using that device again.
2. Contact BingX Support: Use support@bingx.com or the in-app support chat. If you cannot access your account, explain the situation so the security team can help lock it and prevent unauthorized withdrawals.
3. Transfer Assets to a Safe Wallet: If your wallet is exposed, move funds to a secure wallet—preferably a hardware wallet or a new software wallet that has never been used on a compromised device.
4. Report the Scam: Report the incident to BingX Support, your country’s cybercrime authority, such as the FTC in the U.S., and trusted crypto-security communities. Reporting quickly may help block the scammer’s addresses or alert other users before they lose funds.
Conclusion: Stay Informed, Stay Secure
Phishing scams are evolving fast. Chainalysis reports that AI-assisted crypto scams helped push global scam revenues to at least $9.9 billion in 2024, with 2025 showing continued growth as attackers scale phishing campaigns through email, SMS, deepfake calls, and fake apps. The threats are real, but so are the defenses.
Staying safe starts with awareness and ends with action. Follow trusted threat-intelligence sources like Chainalysis, CertiK, and Scam Sniffer, which publish real-time alerts on scam wallets, fake domains, AI-powered phishing campaigns, and wallet drainer activity.
BingX also provides security updates, guides, and platform safety tips through the BingX Blog, BingX Academy, and official social media channels. Checking these regularly gives you early warning about trending scams and new protective features.
Crypto security isn’t just personal; sharing knowledge protects the entire community. Many phishing victims say they “didn’t know what to look for” until it was too late. Teaching friends and family how to spot fake messages, pop-ups, and support impersonators reduces the chances that someone you know becomes the next target.
Quick Recap: How to Protect Yourself
• Stay skeptical of urgent alerts, giveaways, and unknown links
• Bookmark official websites and avoid clicking login links in messages
• Use strong passwords, 2FA, and enable your BingX anti-phishing code
• Turn on the withdrawal whitelist and lock your account if anything looks suspicious
• Keep your phone, browser, and apps updated to block malware
Your BingX account, and your crypto assets, are valuable. A few smart habits and the right security tools go a long way. Stay informed. Stay alert. Stay in control.