As the US Federal Reserve carried out rate cuts since September 2024, many investors are optimistic about Bitcoin's potential price increase. However, the reality is that the Federal Reserve's rate hikes or cuts alone do not directly dictate Bitcoin's price movements. To uncover the true factors driving
Bitcoin price changes, we must look beyond nominal interest rates and delve deeper into underlying influences.
In a high-interest-rate environment, liquidity is tight, making investments less favorable. Conversely, low interest rates typically indicate inflationary conditions, where asset prices tend to rise. Interest rates play a significant role in determining financial market trends, and the cryptocurrency market is no exception. However, focusing solely on the Federal Reserve's nominal interest rates may lead investors to misjudge the true interest rate environment and make poor investment decisions. For investors, the key metric to monitor is the real interest rate, which adjusts nominal rates by accounting for inflation.
What Are Real Interest Rates?
Real interest rates are defined as:
Real Interest Rate = Nominal Interest Rate – Inflation Rate
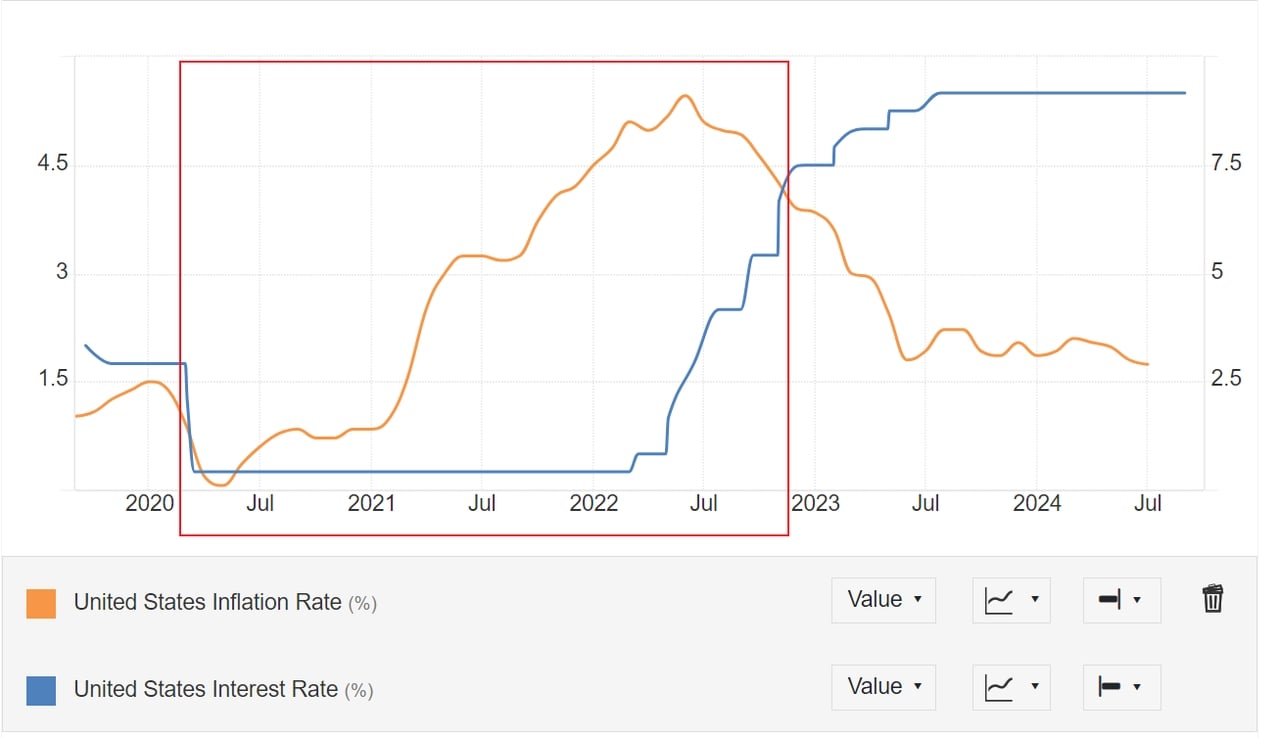
From the chart above, we see that during the period from May 2020 to November 2022, the Federal Reserve's federal funds rate (blue line) was significantly below the inflation rate (yellow line), indicating a very low real interest rate environment. This period saw abundant liquidity, creating favorable conditions for the growth of risk assets like Bitcoin. During this time, Bitcoin's price surged dramatically, with gains exceeding 10x at its peak and over 2x by the end of the period.
However, stopping at this understanding leaves two critical questions unanswered:
1. During the low real interest rate period between May 2020 and November 2022, why did Bitcoin's price experience significant pullbacks?
2. After November 2022, despite rising real interest rates—typically unfavorable for financial markets—why did Bitcoin's price rebound and surpass previous highs by April of this year?
MVRV Z-Score and Bitcoin Price
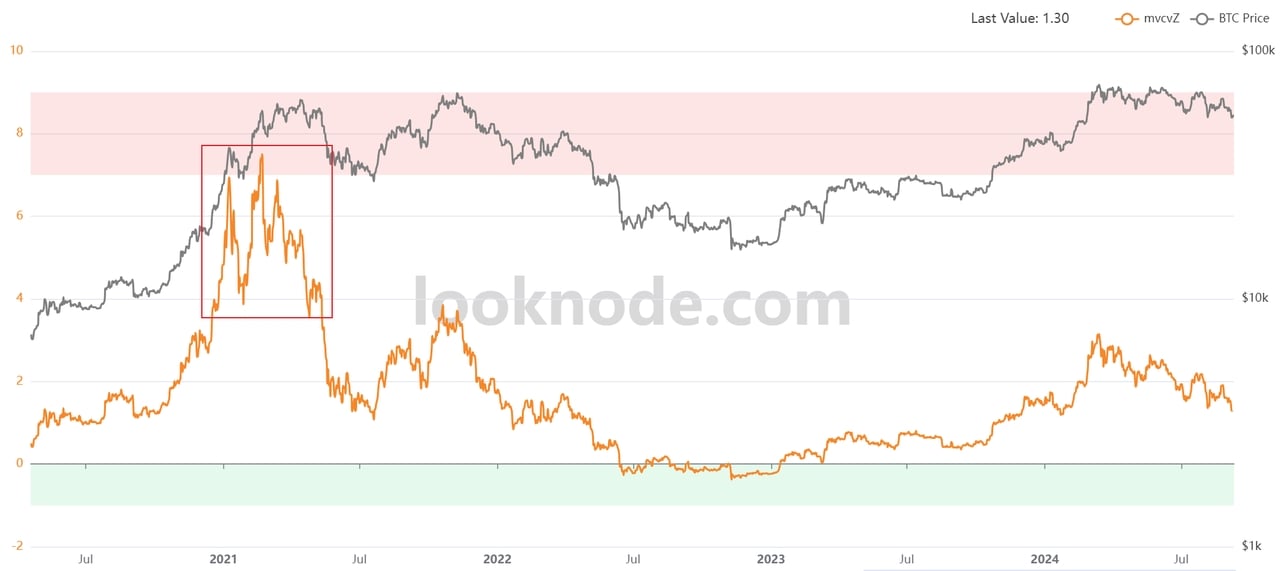
To address the first question: while real interest rates were low between May 2020 and November 2022, no risk asset can sustain perpetual growth. When prices overheat, corrections are inevitable regardless of favorable conditions. The chart below highlights that during this period, Bitcoin’s
MVRV Z-Score (yellow line) climbed sharply, surpassing 7 at its peak. This indicates an overheated market where price pullbacks were unavoidable.
The MVRV Z-Score measures the market's profit-taking sentiment, with higher scores suggesting more profitable investors and lower scores indicating more investors at a loss. For further details on the MVRV Z-Score, refer to the article Understanding Bitcoin’s Value Through MVRV Z-Score.
Hot Money Flow and Bitcoin Price
To address the second question: after November 2022, real interest rates rose, creating a less favorable environment for risk assets. Yet, Bitcoin’s price surged again. This can be explained by another crucial factor influencing risk asset prices: the flow of hot money.
Regardless of an asset’s narrative, price growth requires inflows of capital. Even in an unfavorable interest rate environment, large inflows of hot money can drive asset prices higher in the short term. In the current global economic landscape, movements in the USD/JPY exchange rate often signal the presence of hot money. The rationale lies in Japan’s historically low-interest-rate policy and the Federal Reserve's rate hikes in recent years, creating a significant interest rate differential. Investors borrow yen at low rates, convert to dollars, and invest in financial markets. Profits are amplified as the dollar appreciates, allowing repayment of yen loans with fewer dollars.
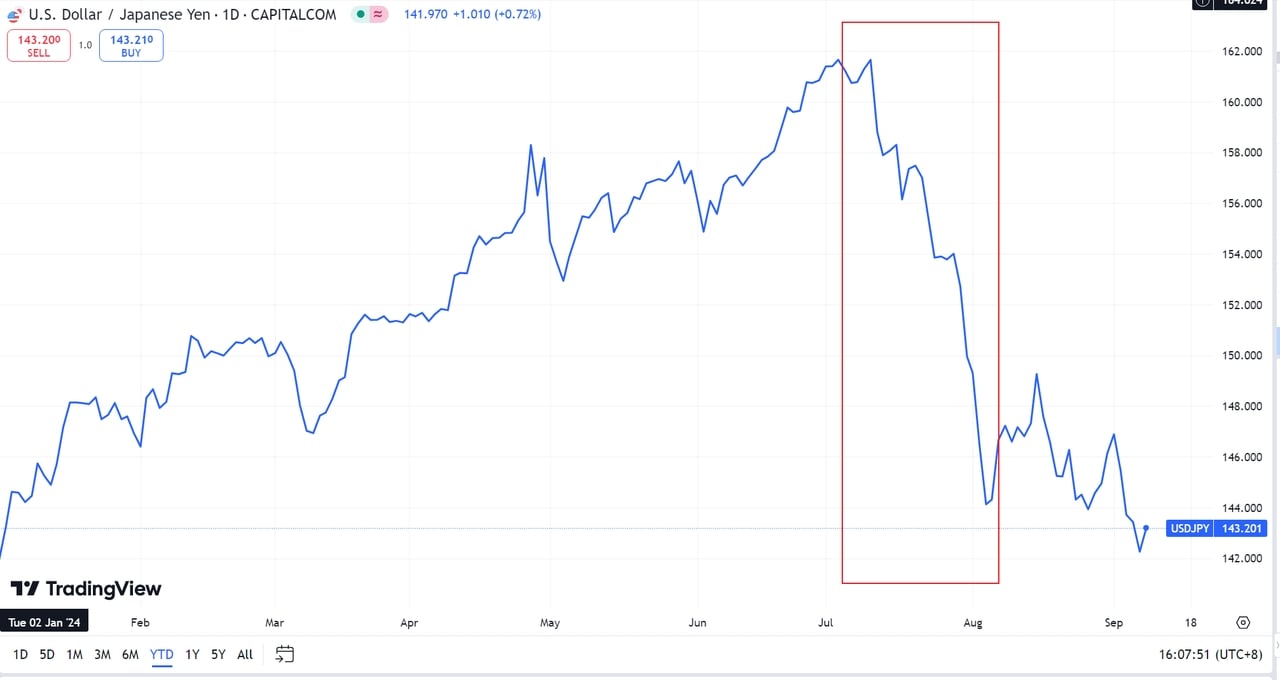
From July this year, however, the yen began appreciating, while the dollar showed signs of depreciation as rate cuts loomed. This narrowing interest rate differential limited the creation of hot money. Consequently, Bitcoin’s price, which had climbed to $55,000 by early September, began to decline. The chart below illustrates the USD/JPY exchange rate’s downward trend starting in July, reflecting a stronger yen and weaker dollar, which has led to Bitcoin’s short-term price volatility.
Conclusion
In summary, real interest rates are a key indicator for evaluating Bitcoin price trends. However, this metric is not flawless and should be considered alongside other indicators like the MVRV Z-Score and USD/JPY exchange rates. Simply assuming that a Fed rate cut will guarantee Bitcoin’s price increase can expose investors to significant risks in the real world. By focusing on real interest rate movements and integrating multiple indicators, investors can more accurately assess Bitcoin’s price trajectory.
Click the image below to receive exclusive gifts up to $6,000 by signing up for a BingX user account.