Uniswap’s UNI token surged over 40% on November 10, 2025 after the “UNIfication” proposal reignited excitement across DeFi. The plan by Uniswap Labs and the Uniswap Foundation activates the long-awaited fee switch, redirecting part of swap fees to the protocol for UNI token burns and treasury revenue. This marks a key moment in Uniswap’s tokenomics, strengthening its role as a sustainable, revenue-generating DeFi ecosystem.
Uniswap is the world’s first major decentralized exchange (DEX) powered by an automated market maker (AMM) model. Built on Ethereum and expanding across Layer-2 networks, it lets anyone swap tokens, provide liquidity, and earn fees without intermediaries. Since its 2018 debut, Uniswap has become a cornerstone of DeFi with billions in total value locked and a leading model for permissionless on-chain trading.
This article explains how Uniswap works, how each version from V1 to the new V4 evolved, and what sets it apart from other DEXs like PancakeSwap and SushiSwap. We’ll also look ahead at Uniswap’s roadmap and what its latest updates mean for the future of decentralized trading.
What Is Uniswap?
Unlike traditional exchanges that use order books, Uniswap operates on an automated market maker (AMM) model powered by smart contracts. These contracts hold token pairs in liquidity pools, allowing users to swap assets instantly at algorithmically determined prices. Liquidity providers (LPs) deposit equal values of two tokens into these pools and earn a share of trading fees in return.
Over time, Uniswap has expanded beyond
Ethereum to
Layer-2 networks such as
Arbitrum,
Optimism, and
Polygon, enabling faster and cheaper trading. Its native governance token, UNI, allows holders to participate in protocol decisions and, through the UNIfication proposal, links protocol revenue to token value.
As of November 2025, Uniswap has grown into a broader ecosystem that includes:
• UniswapX: An open protocol that enables gas-free, auction-based swaps by aggregating liquidity from Uniswap and other DEXs.
• Unichain: A Layer-2 blockchain launched in February 2025 using the OP Stack, designed to scale Uniswap’s liquidity infrastructure and enable native cross-chain trading.
Together, these products position Uniswap as more than a DEX. It is a multi-layer liquidity network shaping the future of decentralized trading.
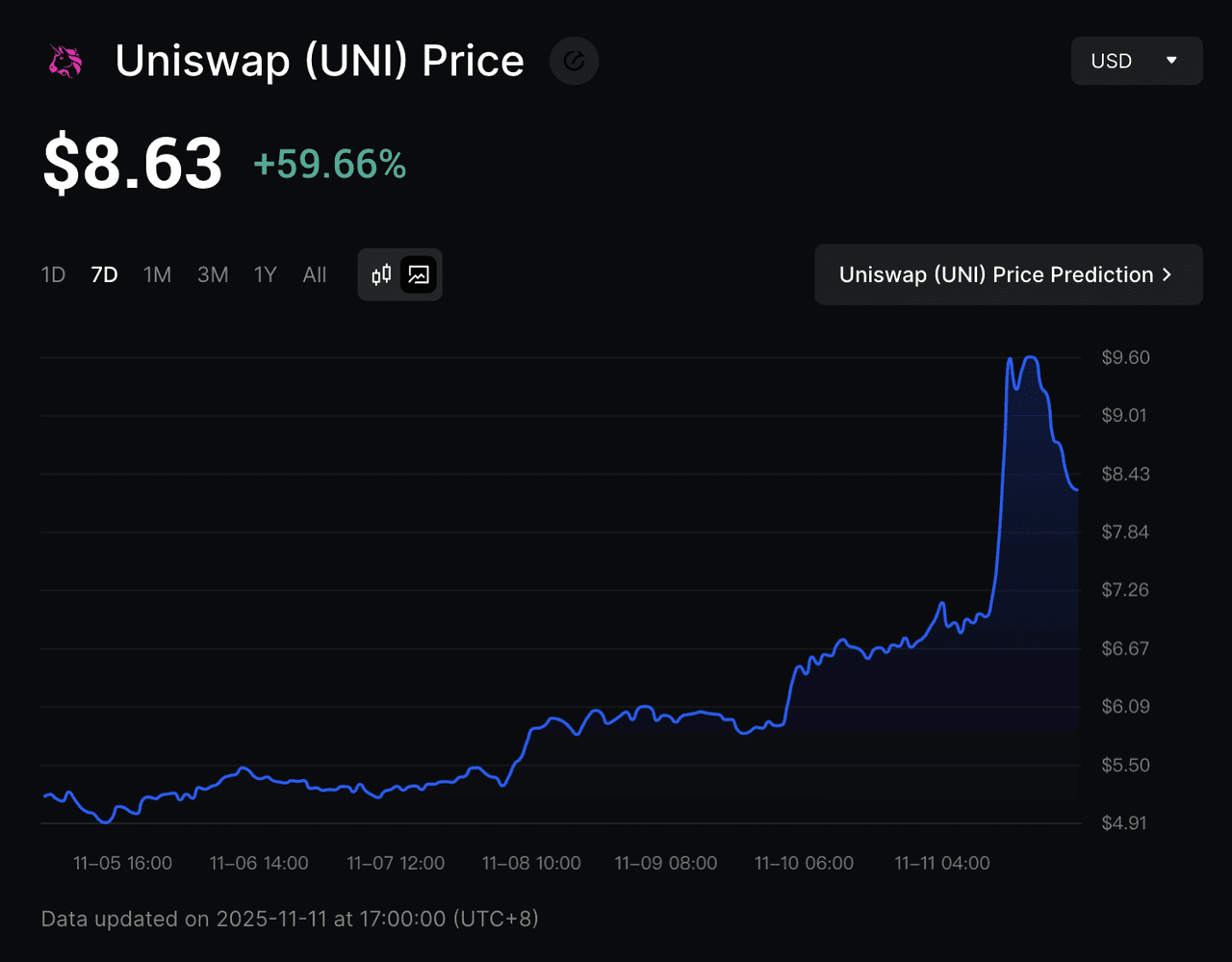
UNIfication Proposal: Uniswap’s Fee Switch Pushes UNI Price Up Over 40% in One Day
On November 10, 2025,
Uniswap’s UNIfication proposal propelled the UNI token from around $6.58 to $9.25 in less than 24 hours, a surge of over 40%. The rally followed an announcement by Uniswap Labs and the Uniswap Foundation to activate the long-awaited fee switch, a mechanism that redirects part of trading fees from liquidity providers to the protocol itself.
Under the new structure, a share of swap fees will be used for UNI token burns and treasury growth, linking network activity directly to token value. This change marks a major turning point in Uniswap’s tokenomics, evolving UNI from a governance token into an asset that reflects real protocol revenue.
Analysts and traders view UNIfication as a step toward sustainable DeFi economics, aligning incentives among liquidity providers, token holders, and developers. The update also cements Uniswap’s position as the leading decentralized exchange (DEX) by volume and innovation, while expanding its presence across Ethereum and Layer-2 ecosystems.
How Does Uniswap DEX Work?
Uniswap operates through smart contracts that automate token trading without any central intermediary. It is built on two key mechanisms: the automated market maker (AMM) and liquidity pools, which together enable instant, permissionless token swaps and yield opportunities such as liquidity farming.
1. Automated Market Maker (AMM): The Algorithm Behind Decentralized Trading
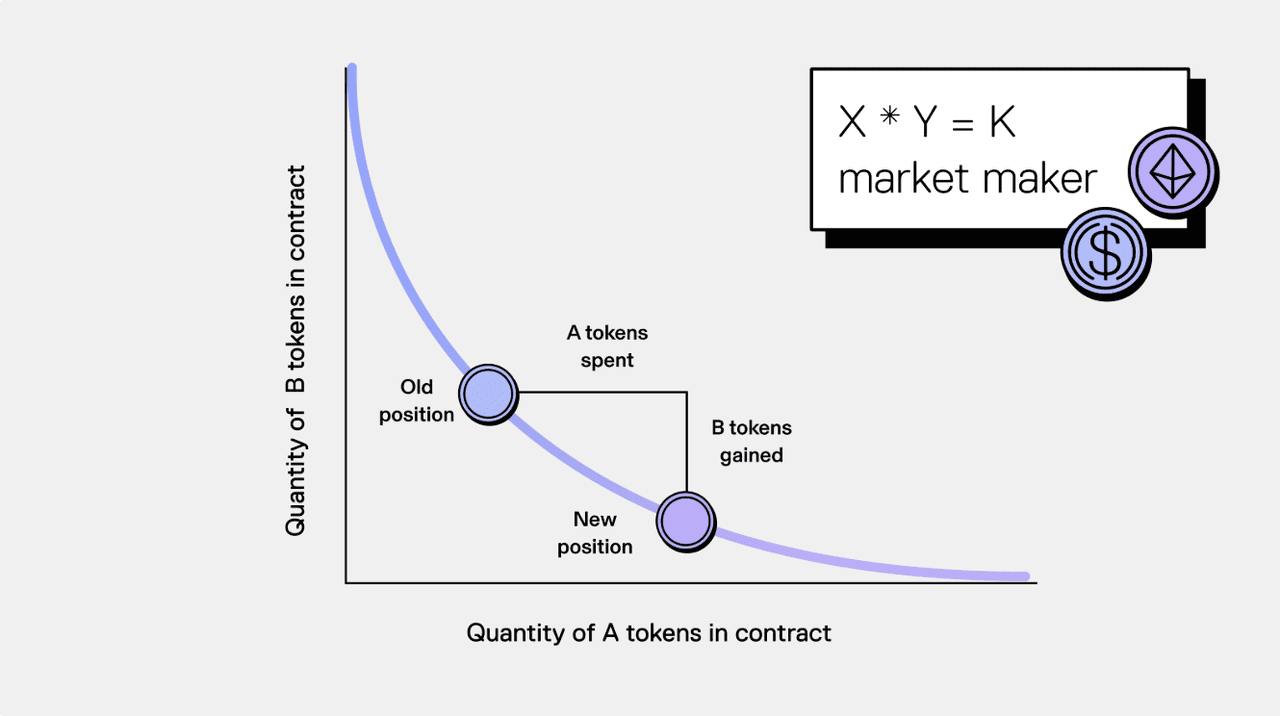
An
automated market maker (AMM) is an algorithm that determines token prices without order books. In Uniswap, the formula x × y = k keeps trading pairs balanced, where x and y are the reserves of each token and k remains constant.
When a user swaps tokens, the pool’s balances change and prices adjust automatically to maintain the constant product. For example, if someone buys ETH with
USDC, the ETH reserve decreases, the USDC reserve increases, and the price of ETH rises accordingly.
This model ensures continuous liquidity and transparent pricing driven by supply and demand, allowing anyone to trade directly on-chain without relying on centralized exchanges.
2. Uniswap Liquidity Pool: The Core of Token Swaps and Liquidity Farming
Each Uniswap liquidity pool holds a pair of tokens such as
ETH/USDC or WBTC/DAI. These pools are funded by liquidity providers (LPs) who deposit equal values of both tokens.
Every trade on the pool generates a 0.3% fee, which is distributed to LPs based on their share of total liquidity. In addition to fees, LPs can participate in
liquidity farming by
staking their pool tokens (LP tokens) in reward programs or governance vaults to earn extra UNI or partner tokens.
While
LPs earn passive income, they also face impermanent loss, which occurs when token prices diverge significantly. Even so, Uniswap’s liquidity pools remain one of the most popular ways for users to earn yield and for traders to access decentralized, always-available liquidity.
Uniswap’s 2020 Airdrop: The First Major Airdrop in Crypto History during DeFi Summer
The DeFi Summer of 2020 marked a period of rapid growth in decentralized finance, driven by
yield farming,
liquidity mining, and the introduction of governance tokens.
Lending protocols like
Compound and
Aave attracted billions in total value locked through token incentives. At the same time, Uniswap V2, launched in May 2020, provided the on-chain infrastructure that powered much of this activity by enabling direct ERC-20 to ERC-20 swaps and permissionless liquidity creation.
In September 2020, Uniswap launched the UNI token airdrop, distributing 400 UNI to every wallet that had ever interacted with the protocol. This came shortly after the rise of SushiSwap, a fork of Uniswap that attempted to attract liquidity providers with aggressive token rewards.
The UNI airdrop became one of the most defining moments in DeFi history. It not only helped Uniswap reclaim its users but also established the “fair airdrop” model, rewarding real protocol participants rather than speculators. This design inspired nearly every airdrop that followed, shaping how decentralized projects approached community ownership.
The UNI airdrop effectively concluded the DeFi Summer era and began a new phase focused on governance, sustainability, and long-term protocol alignment.
What Is UNI Token Used For? Uniswap Token Utilities and Tokenomics Explained
The UNI token is the native governance and utility token of the Uniswap protocol. It was launched in September 2020 through one of DeFi’s most iconic airdrops, rewarding early users who had interacted with the platform before that date. The goal was to decentralize protocol ownership and give the community direct influence over Uniswap’s future development.
After the UNIfication update in 2025, UNI evolved from a governance-only token into a value-accruing asset, linking trading activity to token burns and protocol revenue. This update strengthened Uniswap’s token economy and aligned incentives across users, liquidity providers, and holders.
UNI Tokenomics Overview
Source: Uniswap Blog
• Total Supply: 1 billion UNI tokens
• Circulating Supply: Around 753 million UNI as of November 2025
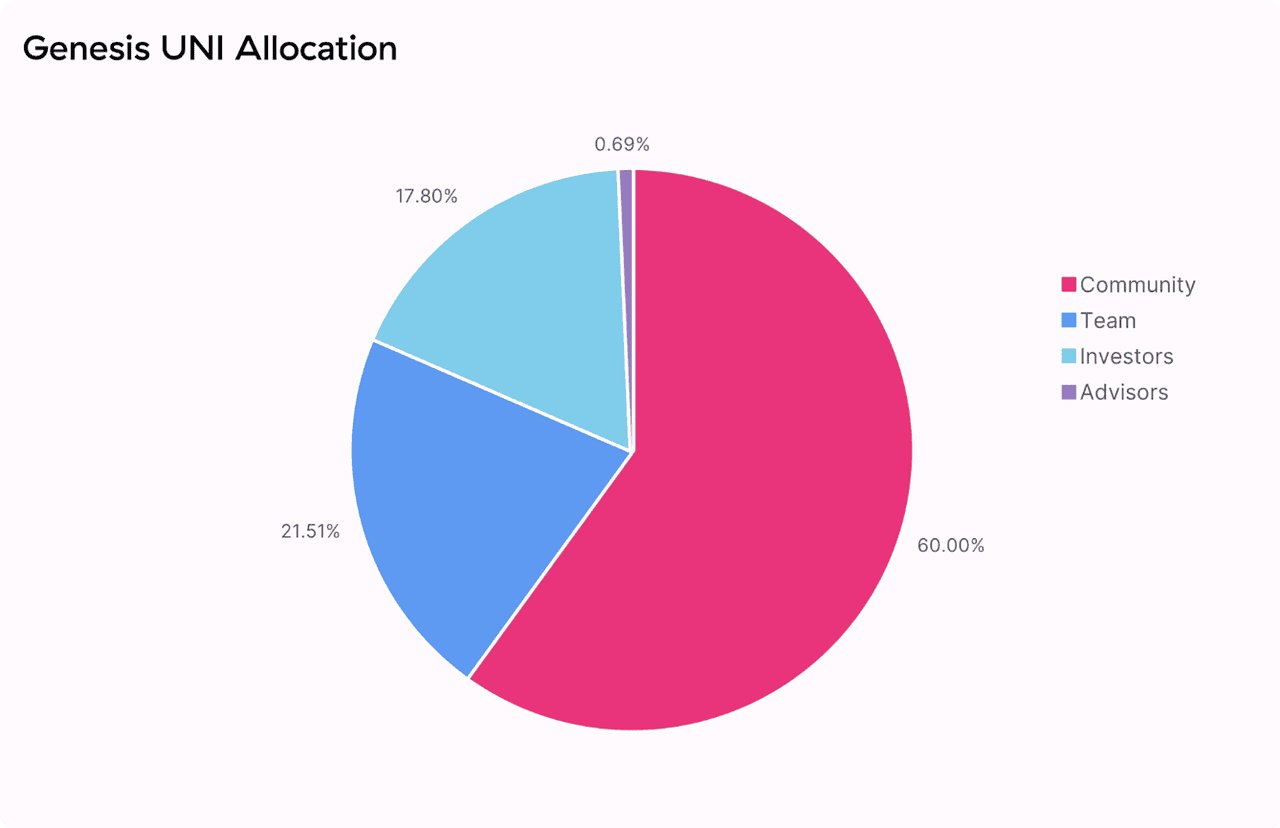
• Initial Allocation: At launch, 60% of UNI was distributed to the community, including users and liquidity providers. Another 21.5% went to team members, 17.8% to investors, and 0.7% to advisors, rewarding both early users and core contributors.
• Vesting Schedule: The four-year vesting period ended in September 2024, ensuring gradual token distribution.
• Burn Mechanism: Introduced under "UNIfication", part of Uniswap’s trading fees is now used for UNI buybacks and burns, reducing supply and linking token value to network activity.
Key Utilities of the UNI Token
• Governance Power: UNI holders can propose and vote on protocol upgrades, fee structures, and treasury spending, keeping Uniswap community-driven.
• Fee Participation: With the fee switch activated under UNIfication, UNI now captures protocol value through token burns and treasury funding tied to trading volume.
• Liquidity Incentives and Farming: UNI rewards are distributed to liquidity providers through liquidity mining programs, encouraging users to supply assets and deepen on-chain liquidity.
• Ecosystem Development: A portion of UNI held in the treasury funds grants, partnerships, and Layer-2 integrations to support continuous innovation across the ecosystem.
Uniswap V1 to V4 Explained: What Are the Key Differences in Features?
Since its launch in 2018, Uniswap has gone through four major upgrades, each improving how decentralized exchanges handle liquidity, efficiency, and user control. From the first automated market maker (AMM) model to today’s programmable liquidity design, Uniswap’s evolution reflects the broader growth of decentralized finance. Below is a complete breakdown of what changed from V1 to V4 and the key features that define each stage.
Uniswap V1: The First On-Chain AMM Exchange
Launched in November 2018, Uniswap V1 introduced the concept of an automated market maker (AMM). Instead of using order books, it relied on liquidity pools that allowed anyone to trade ERC-20 tokens directly on Ethereum.
Each pool paired ETH with one ERC-20 token, so swaps between two ERC-20 tokens required two separate transactions routed through ETH. Though basic, V1 proved that automated liquidity could replace centralized intermediaries.
What’s the Main Features of Uniswap V1
• ETH was the base asset for all trading pairs.
• Constant product formula (x × y = k) set token prices automatically.
• Permissionless liquidity provision for any ERC-20 token.
• Fully on-chain swaps without intermediaries.
Uniswap V2: Expanding Token Pairing and On-Chain Oracles
Released in May 2020, Uniswap V2 removed the ETH-only limitation and introduced several major improvements. It allowed direct ERC-20 to ERC-20 swaps, reduced gas costs, and added on-chain oracles for reliable price feeds.
The upgrade also launched flash swaps, enabling users to borrow tokens and repay within one transaction. V2 became a key driver of the DeFi Summer boom, powering much of the early liquidity in decentralized finance.
What’s the Main Features of Uniswap V2
• Direct ERC-20 to ERC-20 swaps without routing through ETH.
• Time-weighted average price (TWAP) oracles for accurate data.
• Flash swaps for instant, atomic borrowing.
• Improved price and fee tracking for external integrations.
Uniswap V3: Concentrated Liquidity and Capital Efficiency
Launched in May 2021, Uniswap V3 brought a major redesign focused on capital efficiency. It introduced concentrated liquidity, allowing liquidity providers to allocate capital within chosen price ranges instead of across the entire curve.
This model made Uniswap up to 4,000 times more capital efficient than V2 and added multiple fee tiers to accommodate both stable and volatile pairs.
What’s the Main Features of Uniswap V3
• Concentrated liquidity for higher capital efficiency.
• Multiple fee tiers (0.05%, 0.3%, 1%) based on risk profile.
• NFT-based LP positions representing unique price ranges.
• Advanced oracles for more reliable on-chain pricing.
Uniswap V4: Customizable Liquidity Through Hooks
Announced in 2023 and launched on mainnet in 2025, Uniswap V4 introduced hooks, a new system that lets developers customize pool behavior with programmable logic such as dynamic fees, limit orders, or on-chain strategies.
It also adopted a singleton contract architecture, allowing all pools to exist within a single smart contract to save gas and streamline operations. V4 supports native ETH trading and deep integration with Layer-2 networks.
What’s the Main Features of Uniswap V4
• Hooks enable programmable liquidity and custom pool logic.
• Singleton architecture reduces gas and simplifies deployment.
• Native ETH support without wrapping.
• Cross-chain and Layer-2 compatibility for unified liquidity.
Uniswap V4 vs. Uniswap X: What's the Difference?
After the release of Uniswap V4, Uniswap Labs introduced a complementary protocol called Uniswap X, designed to improve trade execution across multiple liquidity sources. While both come from the same ecosystem, they serve different layers of decentralized trading.
Uniswap V4 focuses on the infrastructure layer, offering on-chain programmable liquidity through hooks and a unified singleton architecture. Developers can build customized pools that automate strategies such as dynamic fees, limit orders, or on-chain lending integrations.
Uniswap X, on the other hand, operates at the execution layer. It allows users to perform gas-free swaps through an open auction system where external participants, known as fillers, compete to execute trades at the best available price. Orders are signed off-chain and settled on-chain once completed, protecting users from MEV attacks and failed-transaction costs.
| Feature |
Uniswap V4 |
Uniswap X |
| Core Focus |
On-chain liquidity design |
Off-chain trade execution |
| Launch |
2025 (Mainnet Live) |
2023 (Beta), expanding 2024–2025 |
| Mechanism |
Programmable liquidity via hooks |
Auction-based, gas-free swaps |
| Gas Cost |
Paid by users |
Paid by fillers |
| MEV Protection |
Optional through custom hooks |
Built-in protection through private order flow |
| Liquidity Source |
Uniswap pools on-chain |
Aggregates Uniswap and other DEXs |
| Goal |
Infrastructure for liquidity builders |
Execution layer for traders |
Together, V4 and Uniswap X represent the next step in Uniswap’s evolution, transforming it from a single decentralized exchange into a multi-layer liquidity network where developers build liquidity strategies and traders access the most efficient execution paths across chains.
How to Buy and Trade Uniswap (UNI) on BingX
Whether you want to build a long-term UNI position, trade short-term market swings, or capture opportunities after the UNIfication update, BingX makes it simple with both spot and futures markets. With
BingX AI integrated directly into the interface, you can also access real-time market insights to support smarter trading decisions.
1. Buy or Sell UNI on the Spot Market
If your goal is to accumulate UNI or buy during market pullbacks, the Spot Market is the easiest place to start.
Step 2: Before placing your order, click the AI icon on the chart to activate BingX AI. It will display support and resistance levels, highlight breakout zones, and suggest optimal entry ranges.
Step 3: Choose between a market order for instant execution or a limit order at your preferred entry price. Once filled, your UNI will appear in your BingX wallet, ready to hold, stake, or transfer to an external wallet.
2. Trade UNI with Leverage on Futures
For more active traders, the BingX
Futures Market allows you to go long or short on UNI with leverage, letting you take advantage of both rising and falling prices.
Step 1: Search for
UNI/USDT in the BingX Futures section.
Step 2: Click the AI icon to activate BingX AI. It will analyze momentum, volatility, and trend strength to help you identify potential entry points.
Step 3: Set your leverage, choose your entry price, and place a long (buy) or short (sell) order. Use
stop-loss and take-profit settings to manage risk and lock in profits.
What's Next for Uniswap: Future Roadmap
With Uniswap V4 now live, the protocol has entered a new stage focused on ecosystem integration and token governance under the UNIfication roadmap. This phase represents Uniswap’s shift from version-based development to a long-term framework that connects protocol growth, token value, and governance efficiency.
The UNIfication proposal, approved in late 2025, initiates this transition by activating protocol-level fee sharing, reducing supply through token burns, and consolidating ecosystem operations between the Uniswap Foundation and Uniswap Labs. Together, these steps aim to make Uniswap a unified platform for liquidity and governance across multiple chains.
1. Fee Alignment and Token Supply Reduction: The fee switch is being enabled across select pools, redirecting a portion of trading fees to fund UNI buybacks and burns, strengthening the link between token value and network activity.
2. Unified Governance Structure: The merger of Uniswap Foundation and Uniswap Labs operations is designed to streamline decision-making, accelerate development, and coordinate governance across Ethereum and Layer-2 networks.
3. Ecosystem and Cross-Chain Expansion: Ongoing efforts include supporting the V4 hooks ecosystem and implementing cross-chain governance, enabling Uniswap to serve as the primary liquidity infrastructure for both DeFi and institutional users.
Uniswap’s roadmap now focuses on continuous, protocol-driven innovation, emphasizing sustainable token economics, unified governance, and a modular architecture built for long-term growth.
Related Reading